|
| Title: Astronomy Picture of the Day | |
| friendsoffortiesfive > General > General Discussion | Go to subcategory: |
| Author | Content |
|
Niceguy2
|
|
|
Date Posted:03/06/2014 11:29 PMCopy HTML I really love this site and |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6076 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/13/2025 2:00 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: North - Zhouyue Zhu, South - Lucy Yunxi Hu Explanation: September's total lunar eclipse is tracked across night skies from both the northern and southern hemispheres of planet Earth in these two dramatic timelapse series. In the northern hemisphere sequence (top panel) the Moon’s trail arcs from the upper left to the lower right. It passes below bright planet Saturn, seen under mostly clear skies from the international campus of Zhejiang University in China at about 30 degrees north latitude. In contrast, the southern hemisphere view from Lake Griffin, Canberra, Australia at 35 degrees south latitude, records the Moon’s trail from the upper right to the lower left. Multiple lightning flashes from thunderstorms near the horizon appear reflected in the lake. Both sequences were photographed with 16mm wide-angle lenses and both cover the entire eclipse, with the darkened red Moon totally immersed in Earth's umbral shadow near center. But the different orientations of the Moon’s path across the sky reveal the perspective shifts caused by the views from northern vs. southern latitudes. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6077 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/14/2025 1:49 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Joao Yordanov Serralheiro Explanation: The steerable 60 foot diameter dish antenna of the One-Mile Telescope at Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory, Cambridge, UK, is pointing skyward in this evocative night-skyscape. To capture the dramatic scene, consecutive 30 second exposures were recorded over a period of 90 minutes. Combined, the exposures reveal a background of gracefully arcing star trails that reflect planet Earth's daily rotation on its axis. The North Celestial Pole, the extension of Earth's axis of rotation into space, points near Polaris, the North Star. That's the bright star that creates the short trail near the center of the concentric arcs. But the historic One-Mile Telescope array also relied on planet Earth's rotation to operate. Exploring the universe at radio wavelengths, it was the first radio telescope to use Earth-rotation aperture synthesis. That technique uses the rotation of the Earth to change the relative orientation of the telescope array and celestial radio sources to create radio maps of the sky at a resolution better than that of the human eye. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6078 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/15/2025 1:23 AMCopy HTML 2025 September 14 Video Credit: NASA, Animation: James O'Donoghue (U. Reading) Explanation: How does your favorite planet spin? Does it spin rapidly around a nearly vertical axis, or horizontally, or backwards? The featured video animates NASA images of all eight planets in our Solar System to show them spinning side-by-side for an easy comparison. In the time-lapse video, a day on Earth -- one Earth rotation -- takes just a few seconds. Jupiter rotates the fastest, while Venus spins not only the slowest (can you see it?), but backwards. The inner rocky planets across the top underwent dramatic spin-altering collisions during the early days of the Solar System. Why planets spin and tilt as they do remains a topic of research with much insight gained from modern computer modeling and the recent discovery and analysis of hundreds of exoplanets: planets orbiting other stars. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6079 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/16/2025 2:01 AMCopy HTML 2025 September 15
Video Credit: NASA's SVS, SWRC, CCMC, SWMF; T. Bridgeman et al. Explanation: Can our Sun become dangerous? Yes, sometimes. Every few years our Sun ejects a scary-large bubble of hot gas into the Solar System. Every hundred years or so, when the timing, location, and magnetic field connections are just right, such a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) will hit the Earth. When this happens, the Earth not only experiences dramatic auroras, but its magnetic field gets quickly pushed back and compressed, which causes electric grids to surge. Some of these surges could be dangerous, affecting satellites and knocking out power grids -- which can take months to fix. Just such a storm -- called the Carrington Event -- occurred in 1859 and caused telegraph wires to spark. A similar CME passed near the Earth in 2012, and the featured animated video shows a computer model of what might have happened if it had been a direct hit. In this model, the Earth's magnetopause becomes so compressed that it went inside the orbit of geosynchronous communication satellites. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6080 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/17/2025 1:53 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Daniel Korona Explanation: A newly discovered comet is already visible with binoculars. The comet, C/2025 R2 (SWAN) and nicknamed SWAN25B, is brightening significantly as it emerges from the Sun's direction and might soon become visible on your smartphone -- if not your eyes. Although the brightnesses of comets are notoriously hard to predict, many comets appear brighter as they approach the Earth, with SWAN25B reaching only a quarter of the Earth-Sun distance near October 19. Nighttime skygazers will also be watching for a SWAN25B-spawned meteor shower around October 5 when our Earth passes through the plane of the comet's orbit. The unexpectedly bright comet was discovered by an amateur astronomer in images of the SWAN instrument on NASA's SOHO satellite. The comet is currently best observed in southern skies but is slowly moving north. The featured image was captured at sunset three days ago just above the western horizon in Zacatecas, Mexico. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6081 |
|
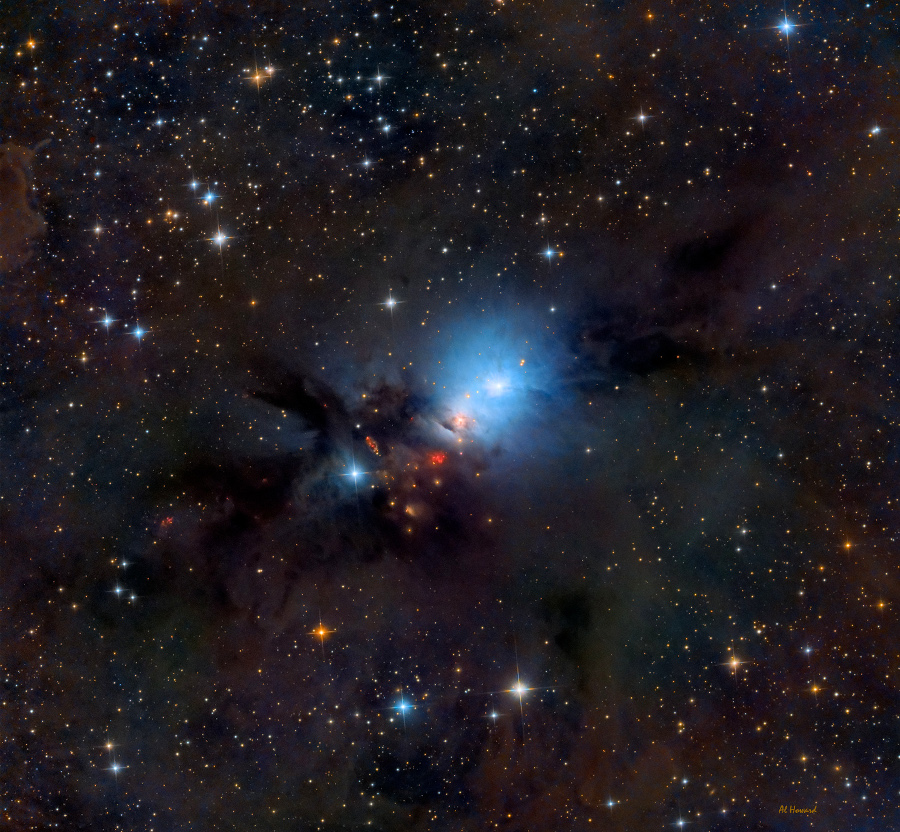
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/18/2025 1:35 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: J. De Winter, C. Humbert, C. Robert & V. Sabet; Text: Ogetay Kayali (MTU) Explanation: Can you spot famous celestial objects in this image? 18th-century astronomer Charles Messier cataloged only two of them: the bright Lagoon Nebula (M8) at the bottom, and the colorful Trifid Nebula (M20) at the upper right. The one on the left that resembles a cat's paw is NGC 6559, and it is much fainter than the other two. Even harder to spot are the thin blue filaments on the left, from supernova remnant (SNR G007.5-01.7). Their glow comes from small amounts of glowing oxygen atoms that are so faint that it took over 17 hours of exposure with just one blue color to bring up. Framing this scene of stellar birth and death are two star clusters: the open cluster M21 just above Trifid, and the globular cluster NGC 6544 at lower left. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6082 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/21/2025 1:25 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Team Ciel Austral Explanation: A new visitor from the outer Solar System, comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN) also known as SWAN25B was only discovered late last week, on September 11. That's just a day before the comet reached perihelion, its closest approach to the Sun. First spotted by Vladimir Bezugly in images from the SWAN instrument on the sun-staring SOHO spacecraft, the comet was surprisingly bright but understandably difficult to see against the Sun's glare. Still close to the Sun on the sky, the greenish coma and tail of C/2025 R2 (SWAN) are captured in this telescopic snapshot from September 17. Spica, alpha star of the constellation Virgo, shines just beyond the upper left edge of the frame while the comet is about 6.5 light-minutes from planet Earth. Near the western horizon after sunset and slightly easier to see in binoculars from the southern hemisphere, this comet SWAN will pass near Zubenelgenubi, alpha star of Libra, on October 2. C/2025 R2 (SWAN) is scheduled to make its closest approach to our fair planet around October 20. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6083 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/21/2025 1:27 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Tommy Lease Explanation: A study in contrasts, this colorful cosmic skyscape features stars, dust, and glowing gas in the vicinity of NGC 6914. The interstellar complex of nebulae lies some 6,000 light-years away, toward the high-flying northern constellation Cygnus and the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy. Obscuring interstellar dust clouds appear in silhouette while reddish hydrogen emission nebulae, along with the dusty blue reflection nebulae, fill the cosmic canvas. Ultraviolet radiation from the massive, hot, young stars of the extensive Cygnus OB2 association ionize the region's atomic hydrogen gas, producing the characteristic red glow as protons and electrons recombine. Embedded Cygnus OB2 stars also provide the blue starlight strongly reflected by the dust clouds. The over one degree wide telescopic field of view spans about 100 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 6914. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6084 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/21/2025 1:29 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Luca Bartek Explanation: Early risers around planet Earth have enjoyed a shining crescent Moon near brilliant Venus, close to the eastern horizon in recent morning twilight skies. And yesterday, on September 19, skygazers watching from some locations in Earth's northern hemisphere were also able to witness Venus, in the inner planet's waxing gibbous phase, pass behind the Moon's waning crescent. In fact, this telescopic snapshot was taken moments before that occultation of gibbous Venus by the crescent Moon began. The close-up view of the beautiful celestial alignment records Venus approaching part of the Moon's sunlit edge in clear daytime skies from the Swiss Alps. Tomorrow, the Sun will pass behind a New Moon. But to witness that partial solar eclipse on September 21, skygazers will need to watch from locations in planet Earth's southern hemisphere. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6085 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/22/2025 1:14 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: Luca Vanzella Explanation: Does the Sun set in the same direction every day? No, the direction of sunset depends on the time of the year. Although the Sun always sets approximately toward the west, on an equinox like tomorrow the Sun sets directly toward the west. After tomorrow's September equinox, the Sun will set increasingly toward the southwest, reaching its maximum displacement at the December solstice. Before tomorrow's September equinox, the Sun had set toward the northwest, reaching its maximum displacement at the June solstice. The featured time-lapse image shows seven bands of the Sun setting one day each month from 2019 December through 2020 June. These image sequences were taken from Alberta, Canada -- well north of the Earth's equator -- and feature the city of Edmonton in the foreground. The middle band shows the Sun setting during an equinox -- in March. From this location, the Sun will set along this same equinox band again tomorrow. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6086 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/23/2025 2:39 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Imran Sultan Explanation: On Saturn, the rings tell you the season. On Earth, today marks an equinox, the time when the Earth's equator tilts directly toward the Sun. Since Saturn's grand rings orbit along the planet's equator, these rings appear most prominent -- from the direction of the Sun -- when the spin axis of Saturn points toward the Sun. Conversely, when Saturn's spin axis points to the side, an equinox occurs, and the edge-on rings are hard to see from not only the Sun -- but Earth. In the featured montage, images of Saturn between the years of 2020 and 2025 have been superposed to show the giant planet passing, with this year's equinox, from summer in the north to summer in the south. Yesterday, Saturn was coincidently about as close as it gets to planet Earth, and so this month the ringed giant's orb is relatively bright and visible throughout the night. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6087 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/24/2025 3:43 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JWST; Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI); Rollover: NASA, ESA, HST, & J. M. Apellániz (IAA, Spain); Acknowledgement: D. De Martin (ESA/Hubble) Explanation: How massive can a normal star be? Estimates made from distance, brightness and standard solar models had given one star in the open cluster Pismis 24 over 200 times the mass of our Sun, making it one of the most massive stars known. This star is the brightest object located in the central cavity near the bottom center of the featured image taken with the Webb Space Telescope in infrared light. For comparison, a rollover image from the Hubble Space Telescope is also featured in visible light. Close inspection of the images, however, has shown that Pismis 24-1 derives its brilliant luminosity not from a single star but from three at least. Component stars would still remain near 100 solar masses, making them among the more massive stars currently on record. Toward the bottom of the image, stars are still forming in the associated emission nebula NGC 6357. Appearing perhaps like a Gothic cathedral, energetic stars near the center appear to be breaking out and illuminating a spectacular cocoon. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6088 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/24/2025 3:43 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JWST; Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI); Rollover: NASA, ESA, HST, & J. M. Apellániz (IAA, Spain); Acknowledgement: D. De Martin (ESA/Hubble) Explanation: How massive can a normal star be? Estimates made from distance, brightness and standard solar models had given one star in the open cluster Pismis 24 over 200 times the mass of our Sun, making it one of the most massive stars known. This star is the brightest object located in the central cavity near the bottom center of the featured image taken with the Webb Space Telescope in infrared light. For comparison, a rollover image from the Hubble Space Telescope is also featured in visible light. Close inspection of the images, however, has shown that Pismis 24-1 derives its brilliant luminosity not from a single star but from three at least. Component stars would still remain near 100 solar masses, making them among the more massive stars currently on record. Toward the bottom of the image, stars are still forming in the associated emission nebula NGC 6357. Appearing perhaps like a Gothic cathedral, energetic stars near the center appear to be breaking out and illuminating a spectacular cocoon. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6089 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/24/2025 3:44 AMCopy HTML
|
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6090 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/25/2025 1:52 AMCopy HTML Illustration Credit: Aurore Simonnet (SSU/EdEon), LVK, URI; LIGO Collaboration Explanation: It was the strongest gravitational wave signal yet measured -- what did it show? GW250114 was detected by both arms of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) in Washington and Louisiana USA earlier this year. Analysis showed that the event was created when two black holes, each of mass around 33 times the mass of the Sun, coalesced into one larger black hole with a mass of around 63 solar masses. Even though the event happened about a billion light years away, the signal was so strong that the spin of all black holes, as well as initial ringing of the final black hole, was deduced with exceptional accuracy. Furthermore, it was confirmed better than before, as previously predicted, that the total event horizon area of the combined black hole was greater than those of the merging black holes. Featured, an artist's illustration depicts an imaginative and conceptual view from near one of the black holes before collision. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6091 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/26/2025 12:35 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Jin Wang Explanation: This year Saturn was at opposition on September 21, opposite the Sun in planet Earth's sky. At its closest to Earth, Saturn was also at its brightest of the year, rising as the Sun set and shining above the horizon all night long among the fainter stars of the constellation Pisces. In this snapshot from the Qinghai Lenghu Observatory, Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China, the outer planet is immersed in a faint, diffuse oval of light known as the gegenschein or counter glow. The diffuse gegenschein is produced by sunlight backscattered by interplanetary dust along the Solar System's ecliptic plane, opposite the Sun in planet Earth's sky. Like a giant eye, on this dark night Saturn and gegenschein seem to stare down on the observatory's telescope domes from their antisolar perspective. Strong atmospheric airglow forms a colorful background along the horizon. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6092 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/27/2025 1:26 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Adam Block Explanation: A new visitor to the inner Solar System, comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN) sports a long ion tail extending diagonally across this almost 7 degree wide telescopic field of view recorded on September 21. A fainter fellow comet also making its inner Solar System debut, C/2025 K1 (ATLAS), can be spotted above and left of SWAN's greenish coma, just visible against the background sea of stars in the constellation Virgo. Both new comets were only discovered in 2025 and are joined in this celestial frame by ruddy planet Mars (bottom), a more familiar wanderer in planet Earth's night skies. The comets may appear to be in a race, nearly neck and neck in their voyage through the inner Solar System and around the Sun. But this comet SWAN has already reached its perihelion or closest approach to the Sun on September 12 and is now outbound along its orbit. This comet ATLAS is still inbound though, and will make its perihelion passage on October 8. Strange, no mention of the interstellar comet, 3I/Atlas, which some scientists think is an alien probe. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6093 |
|
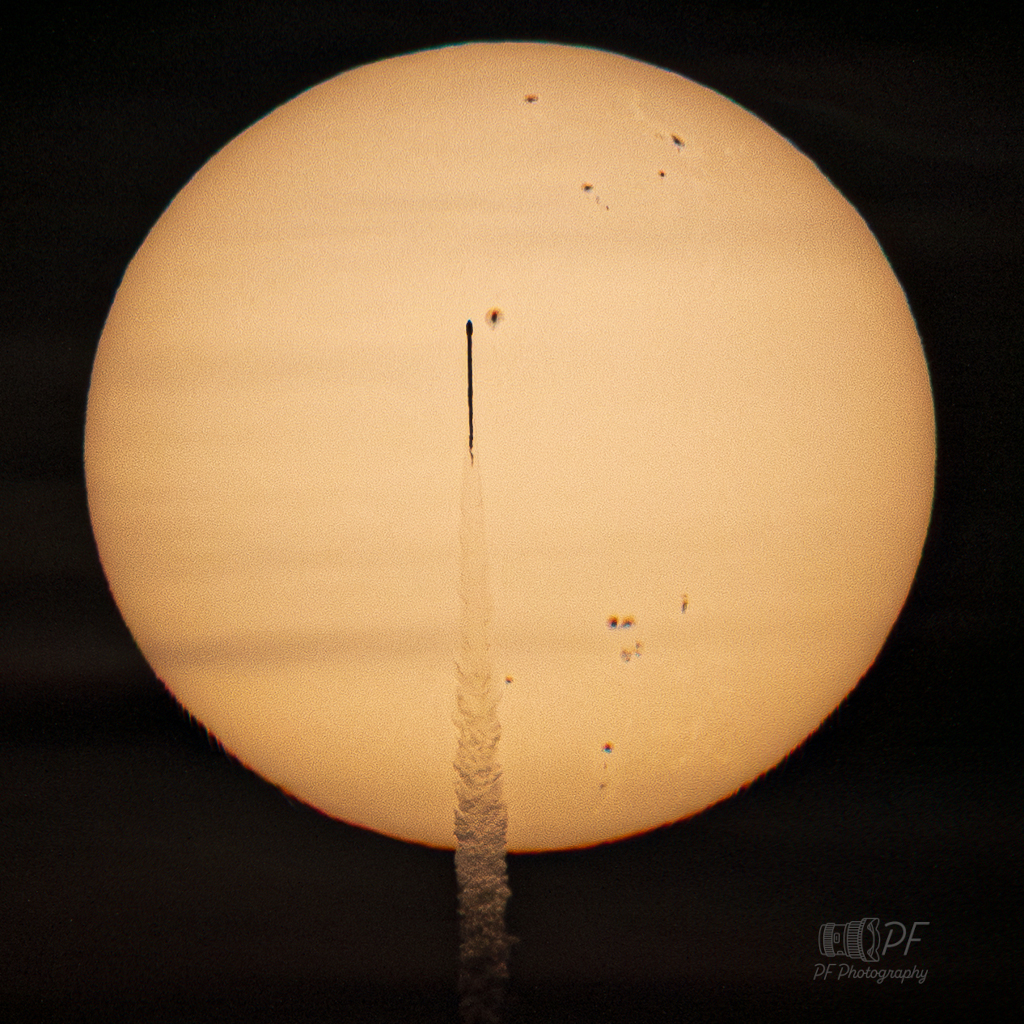
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/28/2025 1:47 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Pascal Fouquet Explanation: On the morning of September 24 a rocket crosses the bright solar disk in this long range telescopic snapshot captured from Orlando, Florida. That's about 50 miles north of its Kennedy Space Center launch site. This rocket carried three new space weather missions to space. Signals have now been successfully acquired from all three - NASA's Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe, NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Follow-On Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) - as they begin their journey to L1, an Earth-Sun lagrange point. L1 is about 1.5 million kilometers in the sunward direction from planet Earth. Appropriately, major space weather influencers, aka dark sunspots in active regions across the Sun, are posing with the transiting rocket. In fact, large active region AR4225 is just right of the rocket's nose. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6094 |
|
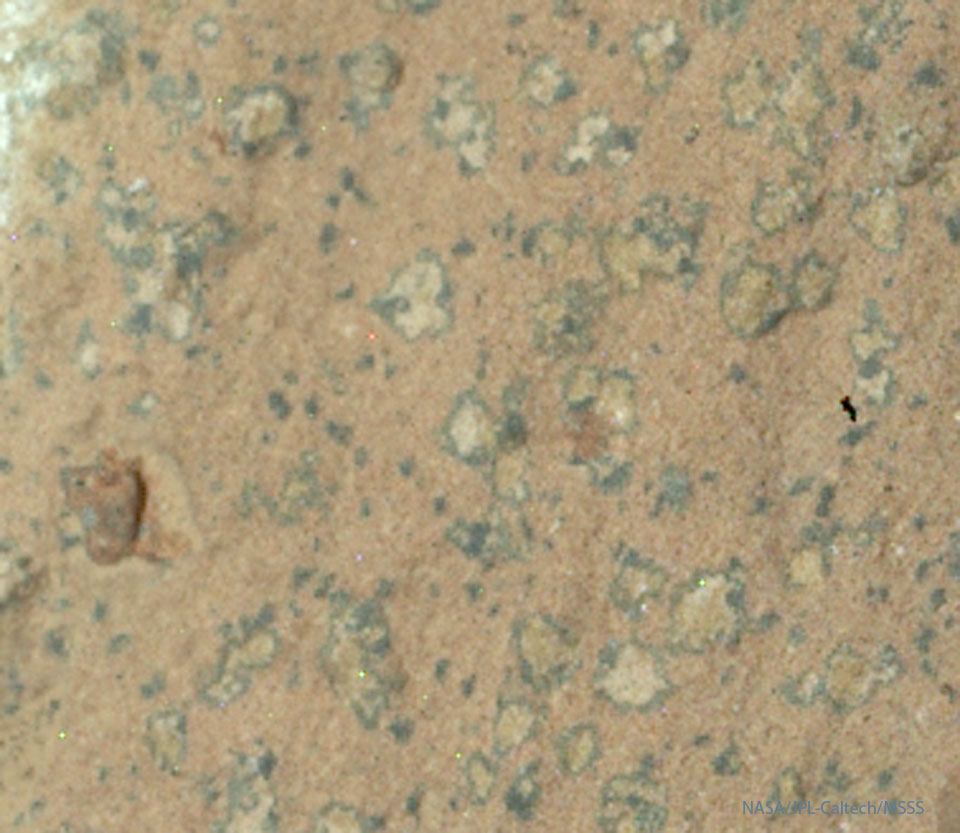
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/29/2025 2:36 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, MSSS, Perseverance Rover Explanation: What is creating these unusual spots? Light-colored spots on Martian rocks, each surrounded by a dark border, were discovered last year by NASA's Perseverance Rover currently exploring Mars. Dubbed leopard spots because of their seemingly similarity to markings on famous Earth-bound predators, these curious patterns are being studied with the possibility they were created by ancient Martian life. The pictured spots measure only millimeters across and were discovered on a larger rock named Cheyava Falls. The exciting but unproven speculation is that long ago, microbes generated energy with chemical reactions that turned rock from red to white while leaving a dark biosignature ring, like some similarly appearing spots on Earth rocks. Although other non-biological explanations have not been ruled out, speculation focusing on this potential biological origin is causing much intrigue. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6095 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:09/30/2025 1:29 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Luc Perrot (TWAN) Explanation: It may look like these comets are racing, but they are not. Comets C/2025 K1 ATLAS (left) and C/2025 R2 SWAN (right) appeared near each other by chance last week in the featured image taken from France's Reunion Island in the southern Indian Ocean. Fainter Comet ATLAS is approaching our Sun and will reach its closest approach in early October when it is also expected to be its brightest -- although still only likely visible with long exposures on a camera. The brighter comet, nicknamed SWAN25B, is now headed away from our Sun, although its closest approach to Earth is expected in mid-October, when optimistic estimates have it becoming bright enough to see with the unaided eye. Each comet has a greenish coma of expelled gas and an ion tail pointing away from the Sun. No mention of 3I/Atlas? |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6096 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/01/2025 12:56 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Victor Sabet & Julien De Winter Explanation: Comet Lemmon is brightening and moving into morning northern skies. Besides Comet SWAN25B and Comet ATLAS, Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is now the third comet currently visible with binoculars and on long camera exposures. Comet Lemmon was discovered early this year and is still headed into the inner Solar System. The comet will round the Sun on November 8, but first it will pass its nearest to the Earth -- at about half the Earth-Sun distance -- on October 21. Although the brightnesses of comets are notoriously hard to predict, optimistic estimates have Comet Lemmon then becoming visible to the unaided eye. The comet should be best seen in predawn skies until mid-October, when it also becomes visible in evening skies. The featured image showing the comet's split and rapidly changing ion tail was taken in Texas, USA late last week. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6097 |
|
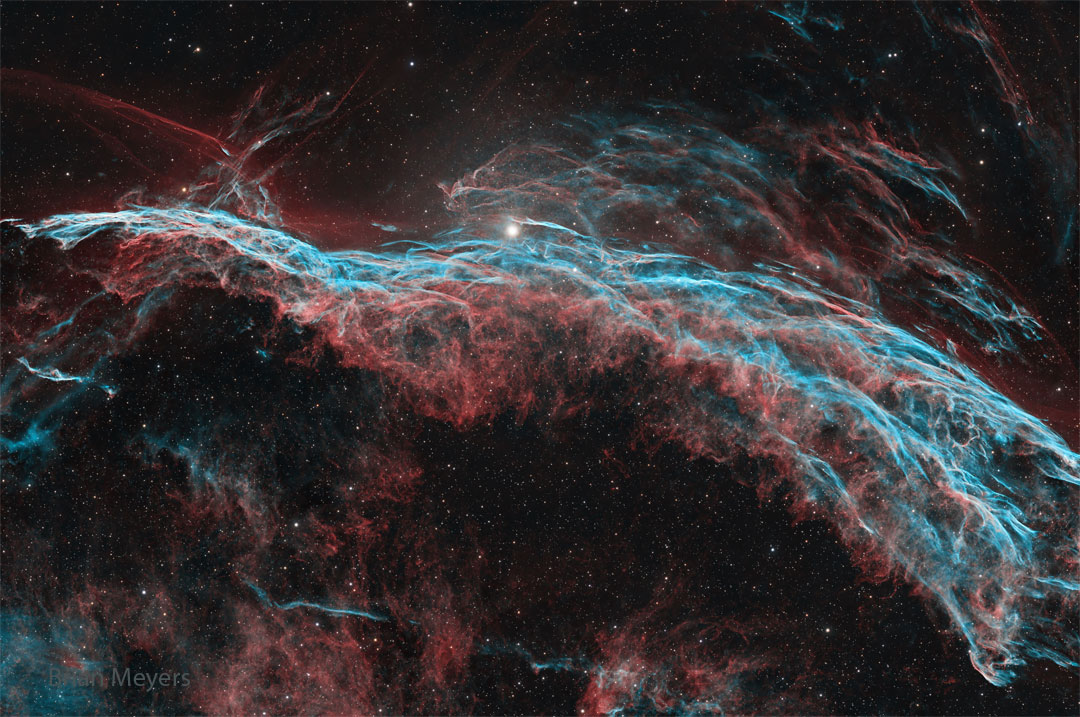
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/02/2025 1:32 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Brian Meyers Explanation: Ten thousand years ago, before the dawn of recorded human history, a new light would suddenly have appeared in the night sky and faded after a few weeks. Today we know this light was from a supernova, or exploding star, and record the expanding debris cloud as the Veil Nebula, a supernova remnant. This sharp telescopic view is centered on a western segment of the Veil Nebula cataloged as NGC 6960 but less formally known as the Witch's Broom Nebula. Blasted out in the cataclysmic explosion, an interstellar shock wave plows through space sweeping up and exciting interstellar material. Imaged with narrow band filters, the glowing filaments are like long ripples in a sheet seen almost edge on, remarkably well separated into atomic hydrogen (red) and oxygen (blue-green) gas. The complete supernova remnant lies about 1400 light-years away towards the constellation Cygnus. This Witch's Broom actually spans about 35 light-years. The bright star in the frame is 52 Cygni, visible with the unaided eye from a dark location but unrelated to the ancient supernova remnant. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#6098 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/04/2025 2:54 AMCopy HTML Due to the lapse in federal government funding, NASA is not updating this website. We sincerely regret this inconvenience. |