| Title: Astronomy Picture of the Day | |
| friendsoffortiesfive > General > General Discussion | Go to subcategory: |
| Author | Content |
|
Niceguy2
|
|
|
Date Posted:03/06/2014 11:29 PMCopy HTML I really love this site and |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5751 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:11/25/2024 3:53 AMCopy HTML 2024 November 24 Video Credit: ESO/MPE/Nick Risinger (skysurvey.org)/VISTA/J. Emerson/Digitized Sky Survey 2 Explanation: What lies at the center of our galaxy? In Jules Verne's science fiction classic, A Journey to the Center of the Earth, Professor Liedenbrock and his fellow explorers encounter many strange and exciting wonders. Astronomers already know of some of the bizarre objects that exist at our Galactic Center, including vast cosmic dust clouds, bright star clusters, swirling rings of gas, and even a supermassive black hole. Much of the Galactic Center is shielded from our view in visible light by the intervening dust and gas, but it can be explored using other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The featured video is actually a digital zoom into the Milky Way's center which starts by utilizing visible light images from the Digitized Sky Survey. As the movie proceeds, the light shown shifts to dust-penetrating infrared and highlights gas clouds that were recently discovered in 2013 to be falling toward the central black hole. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5752 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:11/26/2024 3:15 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Alex Lin (Chilescope) Explanation: One of the most identifiable nebulas in the sky, the Horsehead Nebula in Orion, is part of a large, dark, molecular cloud. Also known as Barnard 33, the unusual shape was first discovered on a photographic plate in the late 1800s. The red glow originates from hydrogen gas predominantly behind the nebula, ionized by the nearby bright star Sigma Orionis. The darkness of the Horsehead is caused mostly by thick dust, although the lower part of the Horsehead's neck casts a shadow to the left. Streams of gas leaving the nebula are funneled by a strong magnetic field. Bright spots in the Horsehead Nebula's base are young stars just in the process of forming. Light takes about 1,500 years to reach us from the Horsehead Nebula. The featured image was taken from the Chilescope Observatory in the mountains of Chile. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5753 |
|
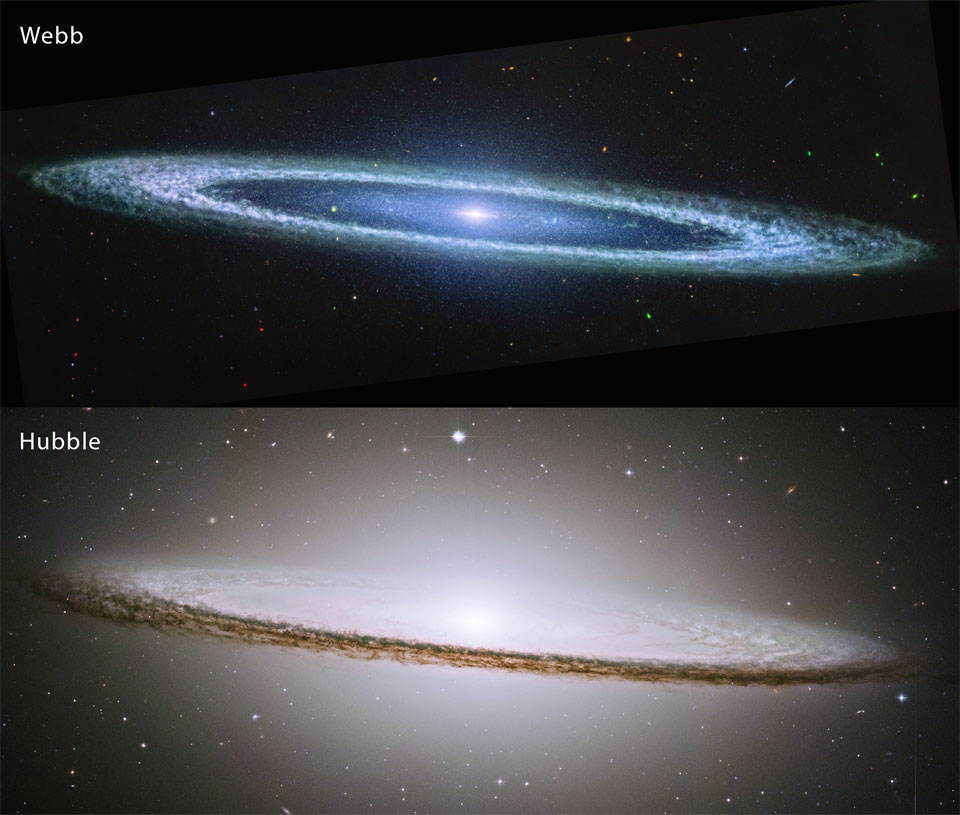
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:11/27/2024 2:46 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Hubble Heritage Project (STScI, AURA) Explanation: This floating ring is the size of a galaxy. In fact, it is a galaxy -- or at least part of one: the photogenic Sombrero Galaxy is one of the largest galaxies in the nearby Virgo Cluster of Galaxies. The dark band of dust that obscures the mid-section of the Sombrero Galaxy in visible light (bottom panel) actually glows brightly in infrared light (top panel). The featured image shows the infrared glow in false blue, recorded recently by the space-based James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and released yesterday, pictured above an archival image taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope in visible light. The Sombrero Galaxy, also known as M104, spans about 50,000 light years and lies 28 million light years away. M104 can be seen with a small telescope in the direction of the constellation Virgo. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5754 |
|
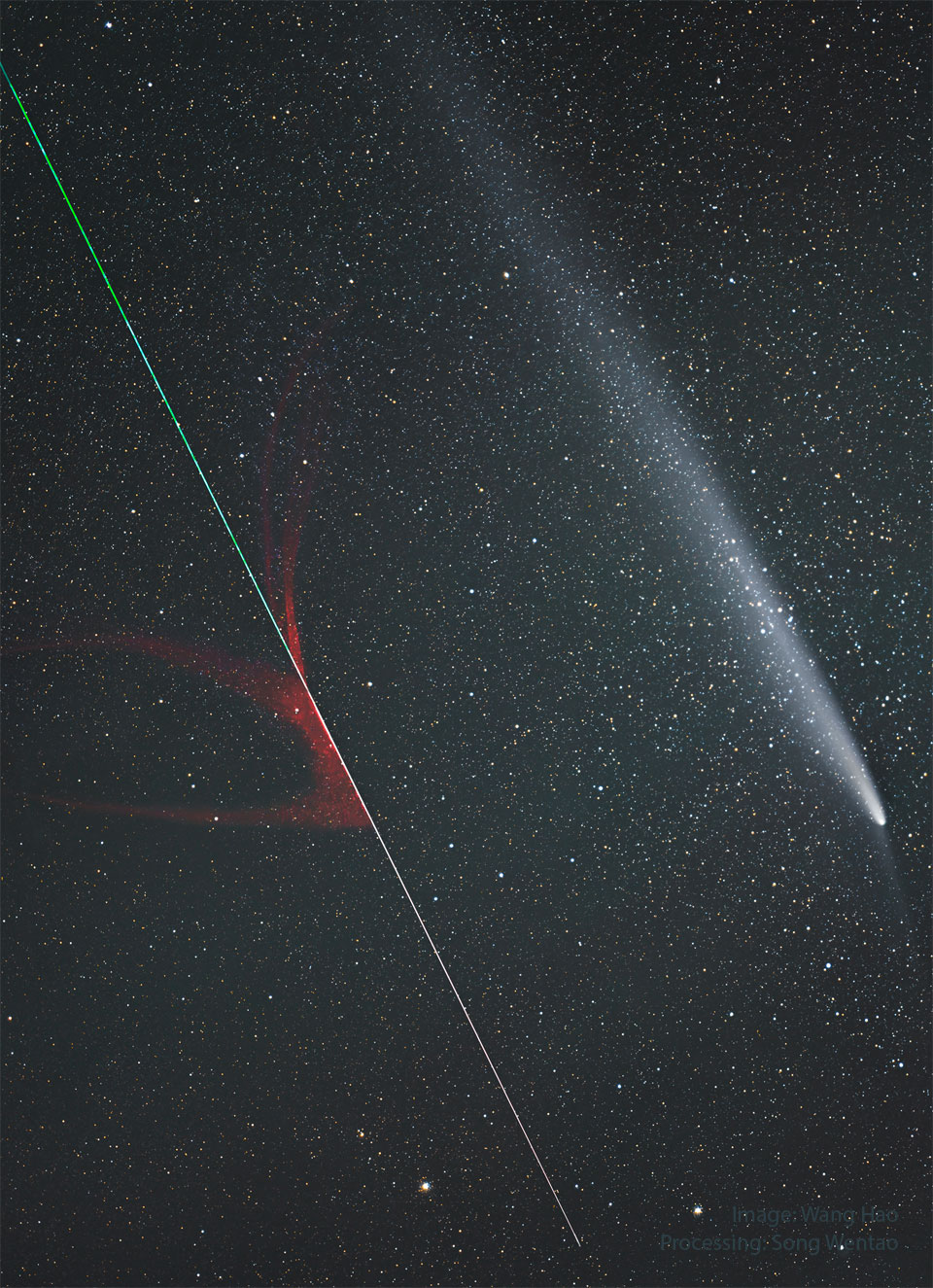
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:11/28/2024 3:30 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Wang Hao; Processing: Song Wentao Explanation: How different are these two streaks? The streak on the upper right is Comet Tsuchinshan-Atlas showing an impressive dust tail. The comet is a large and dirty iceberg that entered the inner Solar System and is shedding gas and dust as it is warmed by the Sun's light. The streak on the lower left is a meteor showing an impressive evaporation trail. The meteor is a small and cold rock that entered the Earth's atmosphere and is shedding gas and dust as it is warmed by molecular collisions. The meteor was likely once part of a comet or asteroid -- perhaps later composing part of its tail. The meteor was gone in a flash and was only caught by coincidence during a series of exposures documenting the comet's long tail. The featured image was captured just over a month ago from Sichuan Province in China. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5755 |
|
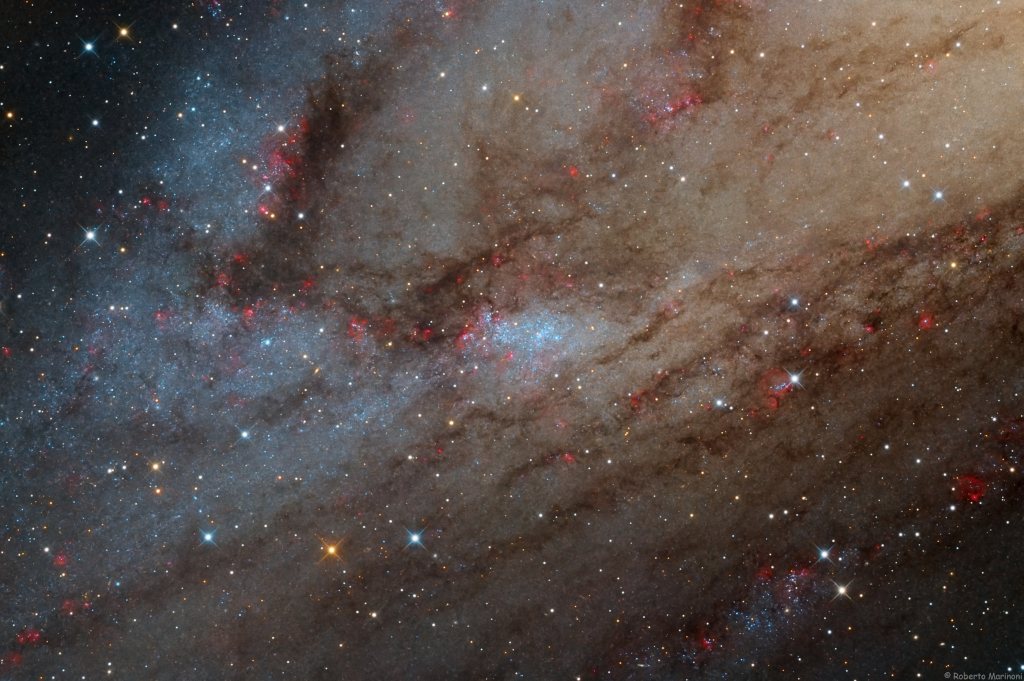
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:11/29/2024 3:22 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Roberto Marinoni Explanation: The large stellar association cataloged as NGC 206 is nestled within the dusty arms of the neighboring Andromeda galaxy along with the galaxy's pinkish star-forming regions. Also known as M31, the spiral galaxy is a mere 2.5 million light-years away. NGC 206 is found at the center of this sharp and detailed close-up of the southwestern extent of Andromeda's disk. The bright, blue stars of NGC 206 indicate its youth. In fact, its youngest massive stars are less than 10 million years old. Much larger than the open or galactic clusters of young stars in the disk of our Milky Way galaxy, NGC 206 spans about 4,000 light-years. That's comparable in size to the giant stellar nurseries NGC 604 in nearby spiral M33 and the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5756 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:11/30/2024 3:39 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Steve Crouch Explanation: Messier 4 can be found west of bright red-giant star Antares, alpha star of the constellation Scorpius. M4 itself is only just visible from dark sky locations, even though the globular cluster of 100,000 stars or so is a mere 5,500 light-years away. Still, its proximity to prying telescopic eyes makes it a prime target for astronomical explorations. Recent studies have included Hubble observations of M4's pulsating cepheid variable stars, cooling white dwarf stars, and ancient, pulsar orbiting exoplanet PSR B1620-26 b. This sharp image was captured with a small telescope on planet Earth. At M4's estimated distance it spans about 50 light-years across the core of the globular star cluster. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5757 |
|
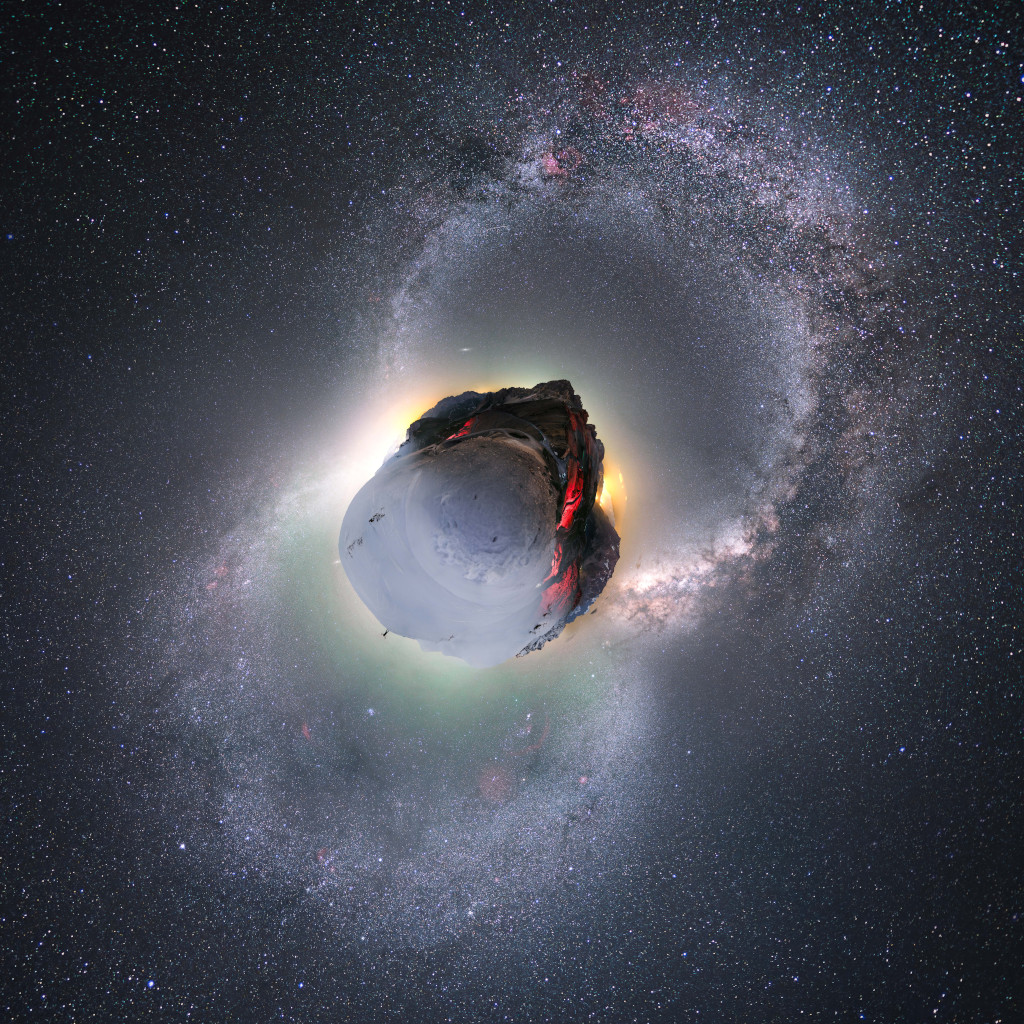
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/01/2024 4:08 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Camille Niel Explanation: Winter and summer appear to come on a single night to this stunning little planet. It's planet Earth of course. The digitally mapped, nadir centered panorama covers 360x180 degrees and is composed of frames recorded during January and July from the Col du Galibier in the French Alps. Stars and nebulae of the northern winter (bottom) and summer Milky Way form the complete arcs traversing the rugged, curved horizon. Cars driving along on the road during a summer night illuminate the 2,642 meter high mountain pass, but snow makes access difficult during winter months except by serious ski touring. Cycling fans will recognize the Col du Galibier as one of the most famous climbs in planet Earth's Tour de France. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5758 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/02/2024 4:14 AMCopy HTML Image Color Credit: Karl Glazebrook & Ivan Baldry (JHU) Explanation: What color is the universe? More precisely, if the entire sky were smeared out, what color would the final mix be? This whimsical question came up when trying to determine what stars are commonplace in nearby galaxies. The answer, depicted here, is a conditionally perceived shade of beige. In computer parlance: #FFF8E7. To determine this, astronomers computationally averaged the light emitted by one of the larger samples of galaxies analyzed: the 200,000 galaxies of the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey. The resulting cosmic spectrum has some emission in all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, but a single perceived composite color. This color has become much less blue over the past 10 billion years, indicating that redder stars are becoming more prevalent. In a contest to better name the color, notable entries included skyvory, univeige, and the winner: cosmic latte. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5759 |
|
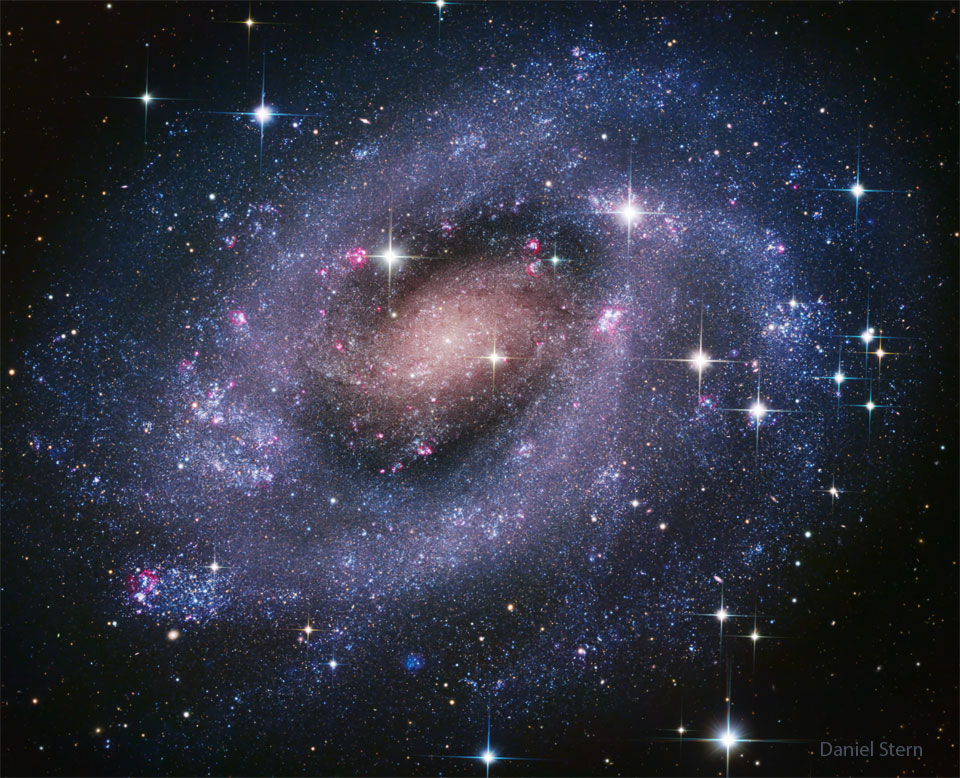
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/03/2024 2:42 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Daniel Stern Explanation: This galaxy is unusual for how many stars it seems that you can see. Stars are so abundantly evident in this deep exposure of the spiral galaxy NGC 300 because so many of these stars are bright blue and grouped into resolvable bright star clusters. Additionally, NGC 300 is so clear because it is one of the closest spiral galaxies to Earth, as light takes only about 6 million years to get here. Of course, galaxies are composed of many more faint stars than bright, and even more of a galaxy's mass is attributed to unseen dark matter. NGC 300 spans nearly the same amount of sky as the full moon and is visible with a small telescope toward the southern constellation of the Sculptor. The featured image was captured in October from Rio Hurtado, Chile and is a composite of over 20 hours of exposure. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5760 |
|
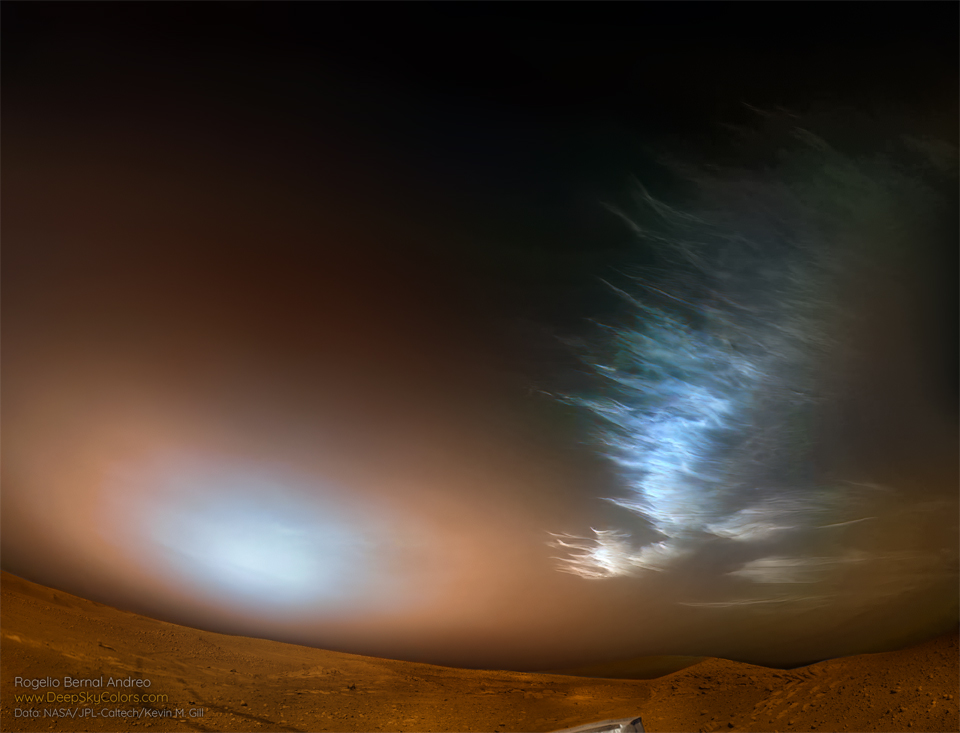
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/04/2024 3:43 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Kevin M. Gill; Processing: Rogelio Bernal Andreo Explanation: If you could stand on Mars -- what might you see? You might look out over a vast orange landscape covered with rocks under a dusty orange sky, with a blue-tinted Sun over the horizon, and odd-shaped water clouds hovering high overhead. This was just the view captured last March by NASA's rolling explorer, Perseverance. The orange coloring is caused by rusted iron in the Martian dirt, some of which is small enough to be swept up by winds into the atmosphere. The blue tint near the rising Sun is caused by blue light being preferentially scattered out from the Sun by the floating dust. The light-colored clouds on the right are likely composed of water-ice and appear high in the Martian atmosphere. The shapes of some of these clouds are unusual for Earth and remain a topic of research. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5761 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/05/2024 3:58 AMCopy HTML 2024 December 4 Video Credit & Copyright: Nick Wright Explanation: Does the Sun return to the same spot on the sky every day? No. A more visual answer is an analemma, a composite of sky images taken at the same time and from the same place over a year. At completion, you can see that the Sun makes a figure 8 on the sky. The featured unusual analemma does not, however, picture the Sun directly: it was created by looking in the opposite direction. All that was required was noting where the shadow of an edge of a house was in the driveway every clear day at the same time. Starting in March in Falcon, Colorado, USA, the photographer methodically marked the shadow's 1 pm location. In one frame you can even see the photographer himself. Although this analemma will be completed in 2025, you can start drawing your own driveway analemma -- using no fancy equipment -- as soon as today. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5762 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/06/2024 3:46 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Marco Lorenzi Explanation: Jupiter looks sharp in these two rooftop telescope images. Both were captured last year on November 17 from Singapore, planet Earth, about two weeks after Jupiter's 2023 opposition. Climbing high in midnight skies the giant planet was a mere 33.4 light-minutes from Singapore. That's about 4 astronomical units away. Jupiter's planet girdling dark belts and light zones are visible in remarkable detail, along with the giant world's whitish oval vortices. Its signature Great Red Spot is prominent in the south. Jupiter rotates rapidly on its axis once every 10 hours. So, based on video frames taken only 15 minutes apart, these images form a stereo pair. Look at the center of the pair and cross your eyes until the separate images come together to see the 3D effect. Of course Jupiter is now not far from its 2024 opposition. Planet Earth is set to pass between the Solar System's ruling gas giant and the Sun on December 7. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5763 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/07/2024 2:53 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Hao Liu (Stanford University) Explanation: Colorful and bright, this streaking fireball meteor was captured in a single exposure taken at Purple Mountain (Tsuchinshan) Observatory’s Xuyi Station in 2020, during planet Earth's annual Perseid meteor shower. The dome in the foreground houses the China Near Earth Object Survey Telescope (CNEOST), the largest multi-purpose Schmidt telescope in China. Located in Xuyi County, Jiangsu Province, the station began its operation as an extension of China's Purple Mountain Observatory in 2006. Darling of planet Earth's night skies in 2024, the bright comet designated Tsuchinshan-ATLAS (C/2023 A3) was discovered in images taken there on 2023 January 9. The discovery is jointly credited to NASA's ATLAS robotic survey telescope at Sutherland Observatory, South Africa. Other comet discoveries associated with the historic Purple Mountain Observatory and bearing the observatory's transliterated Mandarin name include periodic comets 60/P Tsuchinshan and 62/P Tsuchinshan. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5764 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/08/2024 4:17 AMCopy HTML Image and Video Credit: NASA Explanation: You might not think a close up view of rocket engines producing 8.8 million pounds of thrust would be relaxing, but here it can be. In fact, you can get a warm and cozy feeling just spending a few moments watching NASA's holiday rocket engine fireplace. The video features a loop of the Space Launch System rocket's RS-25 main engines throttled up and running flanked by solid rocket boosters and framed by a stone fireplace. The accompanying audio track mixes the drastically muted sounds of the rocket engines firing with the more familiar sounds of a burning, crackling wood fire. AI elements are included in the composed video along with an image and logo from the Artemis I mission. The Artemis I uncrewed mission to the Moon and back again launched in November 2022 on a Space Launch System rocket. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5765 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/09/2024 3:40 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, OPAL Program, J. DePasquale (STScI), L. Lamy (Obs. Paris) Explanation: Are Saturn's auroras like Earth's? To help answer this question, the Hubble Space Telescope and the Cassini spacecraft monitored Saturn's North Pole simultaneously during Cassini's final orbits around the gas giant in September 2017. During this time, Saturn's tilt caused its North Pole to be clearly visible from Earth. The featured image is a composite of ultraviolet images of auroras and optical images of Saturn's clouds and rings, all taken by Hubble. Like on Earth, Saturn's northern auroras can make total or partial rings around the pole. Unlike on Earth, however, Saturn's auroras are frequently spirals -- and more likely to peak in brightness just before midnight and dawn. In contrast to Jupiter's auroras, Saturn's auroras appear better related to connecting Saturn's internal magnetic field to the nearby, variable, solar wind. Saturn's southern auroras were similarly imaged back in 2004 when the planet's South Pole was clearly visible to Earth. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5766 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/10/2024 2:23 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Francesco Pelizzo Explanation: Have you ever seen the Pleiades star cluster? Even if you have, you probably have never seen it as large and clear as this. Perhaps the most famous star cluster on the sky, the bright stars of the Pleiades can be seen with the unaided eye even from the depths of a light-polluted city. With a long exposure from a dark location, though, the dust cloud surrounding the Pleiades star cluster becomes very evident. The featured 23-hour exposure, taken from Fagagna, Italy covers a sky area several times the size of the full moon. Also known as the Seven Sisters and M45, the Pleiades lies about 400 light years away toward the constellation of the Bull (Taurus). A common legend with a modern twist is that one of the brighter stars faded since the cluster was named, leaving only six of the sister stars visible to the unaided eye. The actual number of Pleiades stars visible, however, may be more or less than seven, depending on the darkness of the surrounding sky and the clarity of the observer's eyesight. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5767 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/11/2024 2:02 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: Engraving: Adolf Vollmy; Original Art: Karl Jauslin Explanation: It was a night of 100,000 meteors. The Great Meteor Storm of 1833 was perhaps the most impressive meteor event in recent history. Best visible over eastern North America during the pre-dawn hours of November 13, many people -- including a young Abraham Lincoln -- were woken up to see the sky erupt in streaks and flashes. Hundreds of thousands of meteors blazed across the sky, seemingly pouring out of the constellation of the Lion (Leo). The featured image is a digitization of a wood engraving which itself was based on a painting from a first-person account. We know today that the Great Meteor Storm of 1833 was caused by the Earth moving through a dense part of the dust trail expelled from Comet Tempel-Tuttle. The Earth moves through this dust stream every November during the Leonid meteor shower. Later this week you might get a slight taste of the intensity of that 1833 meteor storm by witnessing the annual Geminid meteor shower. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5768 |
|
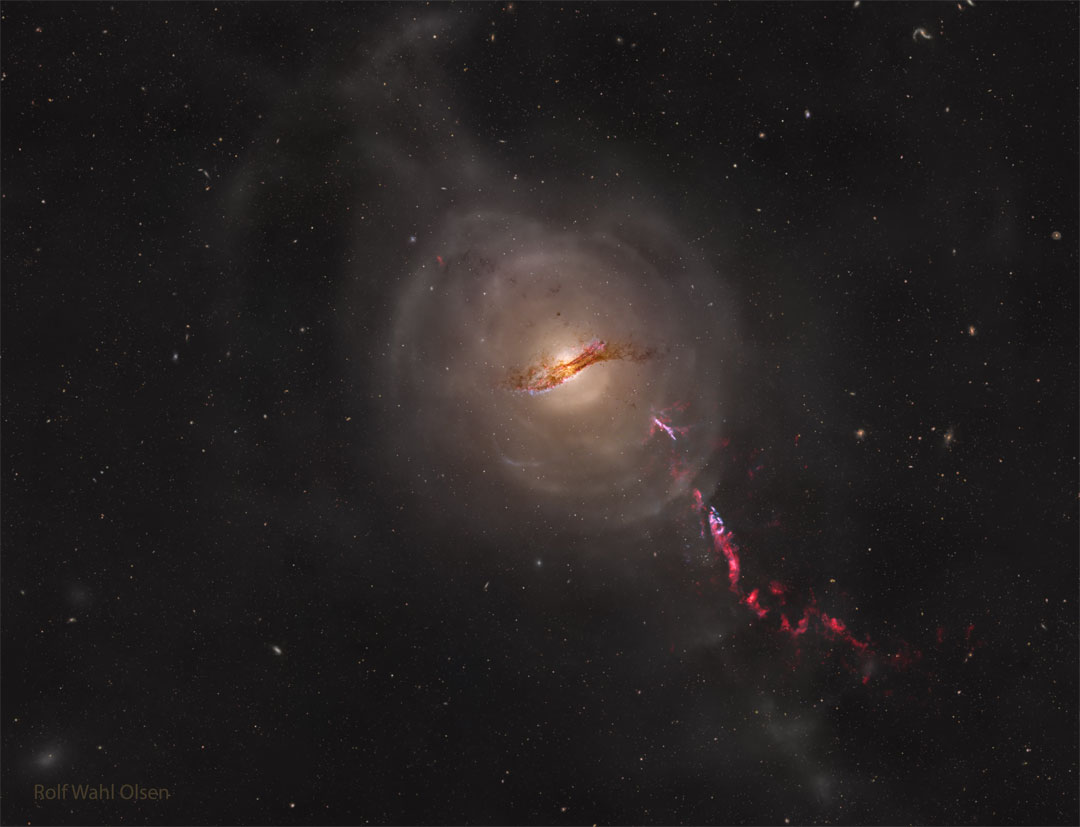
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/12/2024 2:03 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: Rolf Olsen Explanation: What's the closest active galaxy to planet Earth? That would be Centaurus A, cataloged as NGC 5128, which is only 12 million light-years distant. Forged in a collision of two otherwise normal galaxies, Centaurus A shows several distinctive features including a dark dust lane across its center, outer shells of stars and gas, and jets of particles shooting out from a supermassive black hole at its center. The featured image captures all of these in a composite series of visible light images totaling over 310 hours captured over the past 10 years with a homebuilt telescope operating in Auckland, New Zealand. The brightness of Cen A's center from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma rays underlies its designation as an active galaxy. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5769 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/12/2024 2:03 AMCopy HTML
|
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5770 |
|
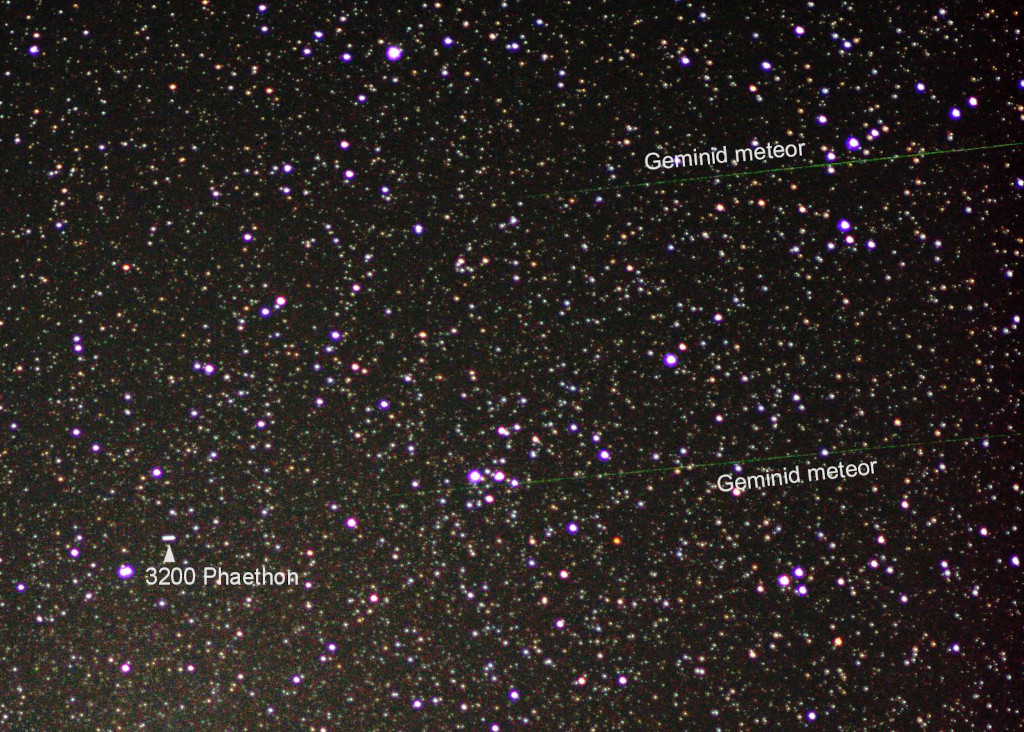
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/13/2024 3:01 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Mikiya Sato (Nippon Meteor Society) Explanation: Based on its well-measured orbit, 3200 Phaethon (sounds like FAY-eh-thon) is recognized as the source of the meteoroid stream responsible for the annual Geminid meteor shower. Even though most meteor shower parents are comets, 3200 Phaethon is a known and closely tracked near-Earth asteroid with a 1.4 year orbital period. Rocky and sun-baked, its perihelion or closest approach to the Sun is well within the orbit of innermost planet Mercury. In this telescopic field of view, the asteroid's rapid motion against faint background stars of the heroic constellation Perseus left a short trail during the two minute total exposure time. The (faint) parallel streaks of its meteoric children flashed much more quickly across the scene. The family portrait was recorded near the Geminid meteor shower's very active peak on 2017 December 13. That was just three days before 3200 Phaethon's historic close approach to planet Earth. This year, the night of December 13 should again see the peak of the Geminid meteor shower, but faint meteors will be washed out by the bright light of the nearly full moon. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5771 |
|
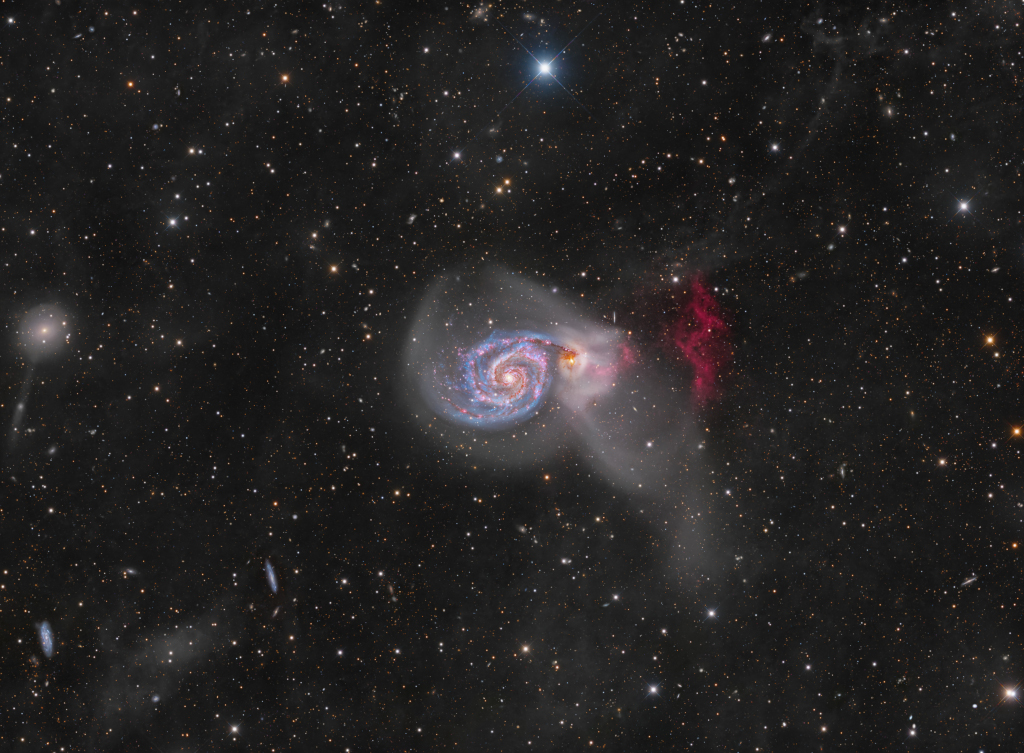
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/14/2024 3:56 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: The Deep Sky Collective - Tim Schaeffer, Carl Björk, Steeve Body, Fabian Neyer, Aki Jain, Ryan Wierckx, Paul Kent, Brian Valente, Antoine & Dalia Grelin, Nicolas Puig, Stephen Guberski, Mike Hamende, Julian Shapiro, John Dziuba, Mikhail Vasilev, Bogdan Borz, Adrien Keijzer Explanation: An intriguing pair of interacting galaxies, M51 is the 51st entry in Charles Messier's famous catalog. Perhaps the original spiral nebula, the large galaxy with whirlpool-like spiral structure seen nearly face-on is also cataloged as NGC 5194. Its spiral arms and dust lanes sweep in front of its smaller companion galaxy, NGC 5195. Some 31 million light-years distant, within the boundaries of the well-trained constellation Canes Venatici, M51 looks faint and fuzzy to the eye in direct telescopic views. But this remarkably deep image shows off stunning details of the galaxy pair's striking colors and fainter tidal streams. The image includes extensive narrowband data to highlight a vast reddish cloud of ionized hydrogen gas recently discovered in the M51 system and known to some as the H-alpha cliffs. Foreground dust clouds in the Milky Way and distant background galaxies are captured in the wide-field view. A continuing collaboration of astro-imagers using telescopes on planet Earth assembled over 3 weeks of exposure time to create this evolving portrait of M51. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5772 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/15/2024 1:33 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: Apollo 17, NASA, (Image Reprocessing: Andy Saunders) Explanation: Awkward and angular looking, Apollo 17's lunar module Challenger was designed for flight in the near vacuum of space. Digitally enhanced and reprocessed, this picture taken from Apollo 17's command module America shows Challenger's ascent stage in lunar orbit. Small reaction control thrusters are at the sides of the moonship with the bell of the ascent rocket engine underneath. The hatch allowing access to the lunar surface is seen at the front, with a round radar antenna at the top. Mission commander Gene Cernan is clearly visible through the triangular window. This spaceship performed gracefully, landing on the Moon and returning the Apollo astronauts to the orbiting command module in December of 1972. So where is Challenger now? Its descent stage remains at the Apollo 17 landing site in the Taurus-Littrow valley. The ascent stage pictured was intentionally crashed nearby after being jettisoned from the command module prior to the astronauts' return to planet Earth. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5773 |
|
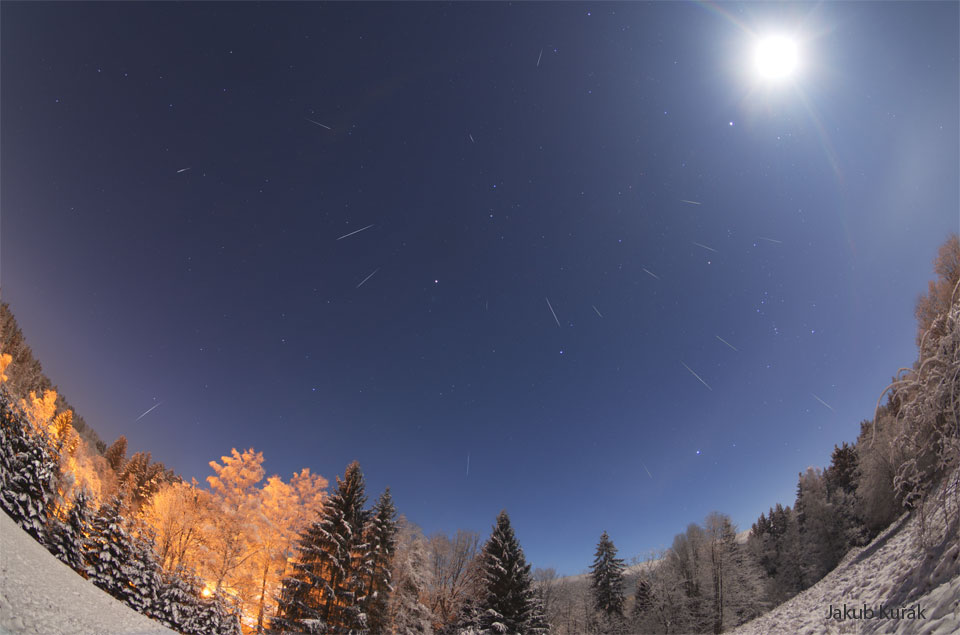
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/16/2024 2:10 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Jakub Kuřák Explanation: Meteors have been flowing out from the constellation Gemini. This was expected, as mid-December is the time of the Geminid Meteor Shower. Pictured here, over two dozen meteors were caught in successively added exposures taken over several hours early Saturday morning from a snowy forest in Poland. The fleeting streaks were bright enough to be seen over the din of the nearly full Moon on the upper right. These streaks can all be traced back to a point on the sky called the radiant toward the bright stars Pollux and Castor in the image center. The Geminid meteors started as sand sized bits expelled from asteroid 3200 Phaethon during its elliptical orbit through the inner Solar System. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5774 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/16/2024 2:10 AMCopy HTML
|
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5775 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:12/17/2024 2:29 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Licence (CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO): ESA, Rosetta spacecraft, NAVCAM; Additional Processing: Stuart Atkinson Explanation: This kilometer high cliff occurs on the surface of a comet. It was discovered on the dark nucleus of Comet Churyumov - Gerasimenko (CG) by Rosetta, a robotic spacecraft launched by ESA, which orbited the comet from 2014 to 2016. The ragged cliff, as featured here, was imaged by Rosetta early in its mission. Although towering about one kilometer high, the low surface gravity of Comet CG would likely make a jump from the cliffs by a human survivable. At the foot of the cliffs is relatively smooth terrain dotted with boulders as large as 20 meters across. Data from Rosetta indicates that the ice in Comet CG has a significantly different deuterium fraction -- and hence likely a different origin -- than the water in Earth's oceans. The probe was named after the Rosetta Stone, a rock slab featuring the same text written in three different languages that helped humanity decipher ancient Egyptian writing. |