| Title: Astronomy Picture of the Day | |
| friendsoffortiesfive > General > General Discussion | Go to subcategory: |
| Author | Content |
|
Niceguy2
|
|
|
Date Posted:03/06/2014 11:29 PMCopy HTML I really love this site and |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5701 |
|
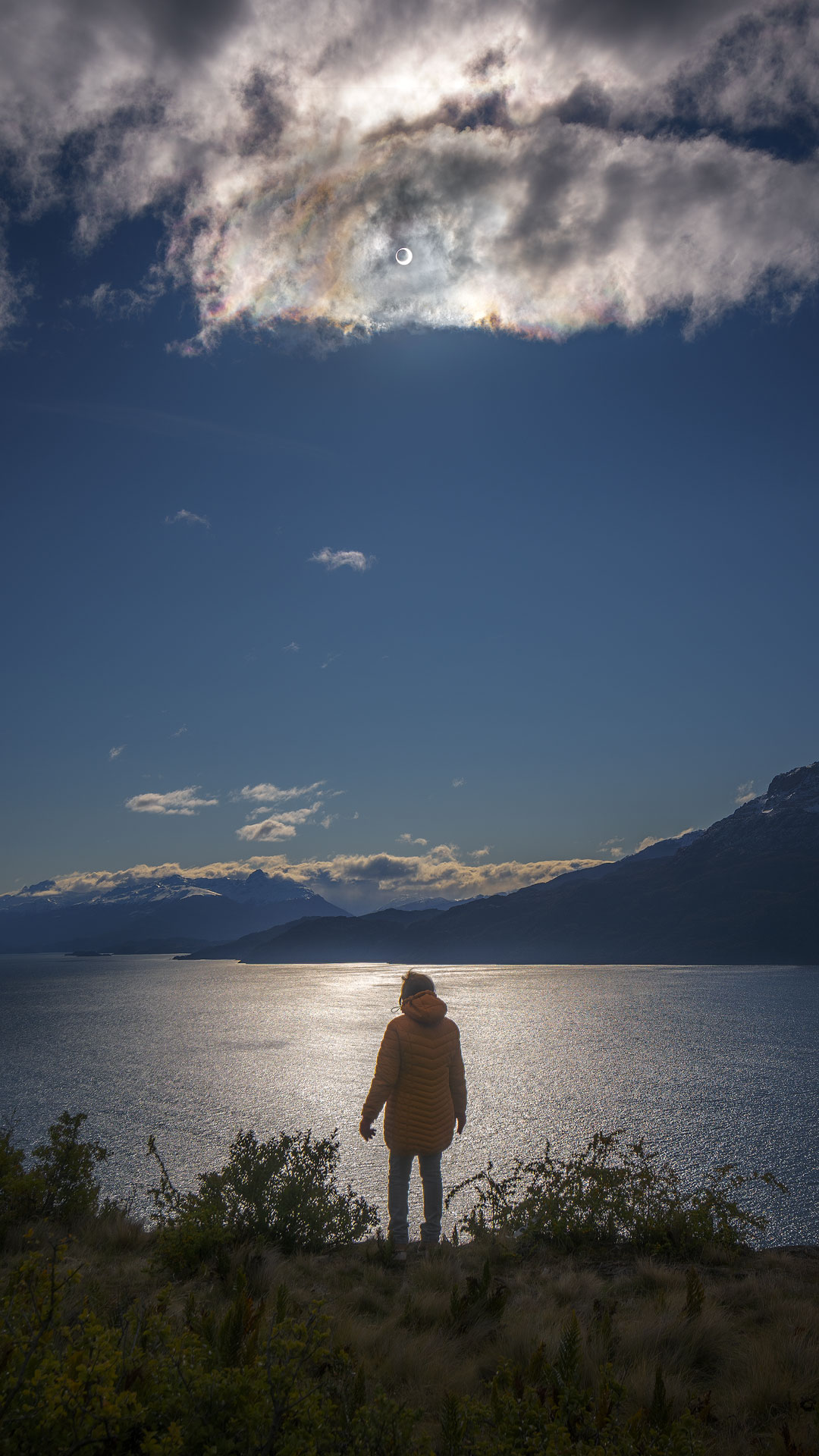
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/09/2024 12:36 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Alexis Trigo Explanation: Can you find the Sun? OK, but can you explain why there’s a big dark spot in the center? The spot is the Moon, and the impressive alignment shown, where the Moon lines up inside the Sun, is called an annular solar eclipse. Such an eclipse occurred just last week and was visible from a thin swath mostly in Earth's southern hemisphere. The featured image was captured from Patagonia, Chile. When the Moon is significantly closer to the Earth and it aligns with the Sun, a total solar eclipse is then visible from parts of the Earth. Annular eclipses are slightly more common than total eclipses, but as the Moon moves slowly away from the Earth, before a billion more years, the Moon's orbit will no longer bring it close enough for a total solar eclipse to be seen from anywhere on Earth. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5702 |
|
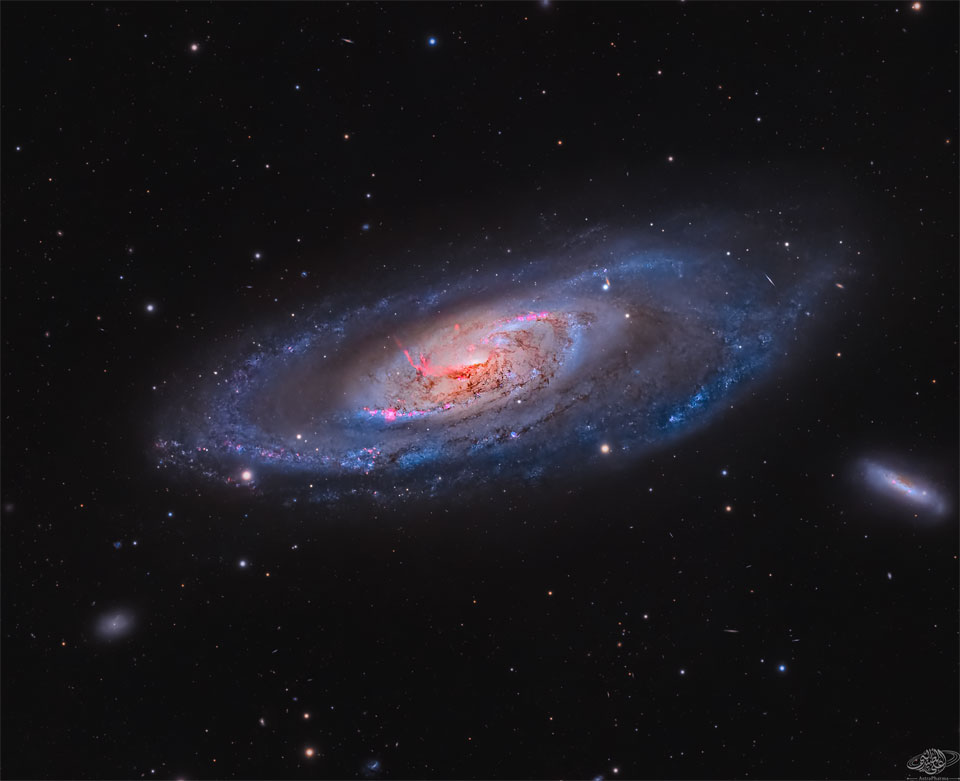
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/10/2024 2:14 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Ali Al Obaidly Explanation: What's happening at the center of spiral galaxy M106? A swirling disk of stars and gas, M106's appearance is dominated by blue spiral arms and red dust lanes near the nucleus, as shown in the featured image taken from the Kuwaiti desert. The core of M106 glows brightly in radio waves and X-rays where twin jets have been found running the length of the galaxy. An unusual central glow makes M106 one of the closest examples of the Seyfert class of galaxies, where vast amounts of glowing gas are thought to be falling into a central massive black hole. M106, also designated NGC 4258, is a relatively close 23.5 million light years away, spans 60 thousand light years across, and can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of the Hunting Dogs (Canes Venatici). |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5703 |
|
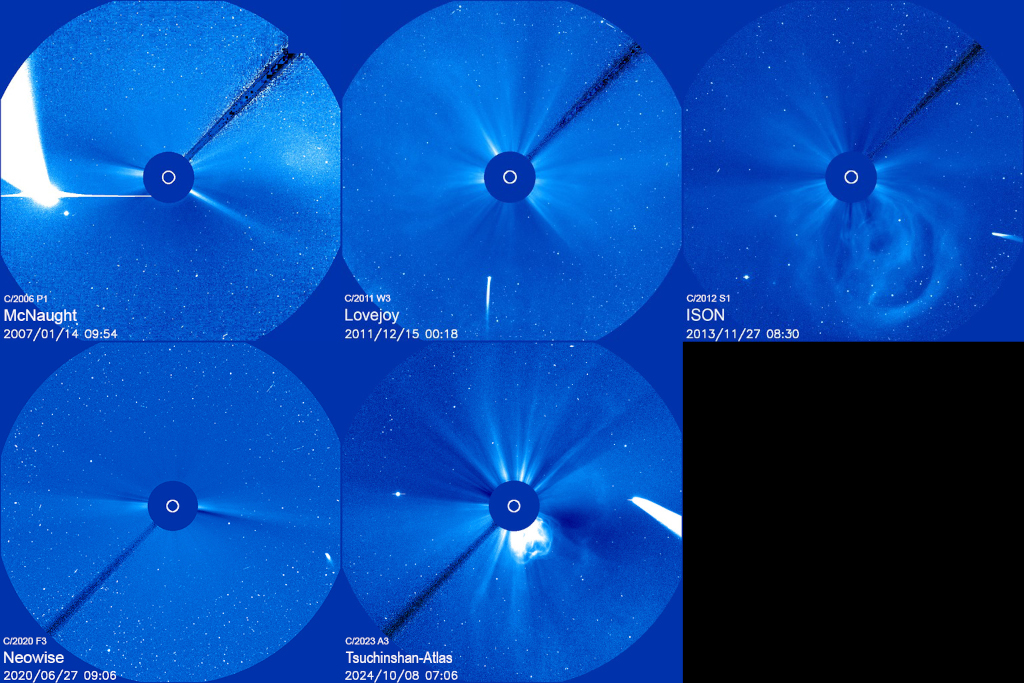
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/11/2024 3:47 AMCopy HTML Image Compilation Credit: Tunc Tezel (TWAN) Explanation: Five bright comets are compared in these panels, recorded by a coronograph on board the long-lived, sun-staring SOHO spacecraft. Arranged chronologically all are recognizable by their tails streaming away from the Sun at the center of each field of view, where a direct view of the overwhelmingly bright Sun is blocked by the coronagraph's occulting disk. Each comet was memorable for earthbound skygazers, starting at top left with Comet McNaught, the 21st century's brightest comet (so far). C/2023 A3 Tsuchinshan-Atlas, approaching its perihelion with the active Sun at bottom center, has most recently grabbed the attention of comet watchers around the globe. By the end of October 2024, the blank 6th panel may be filled with bright sungrazer comet C/2024 S1 Atlas. ... or not. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5704 |
|
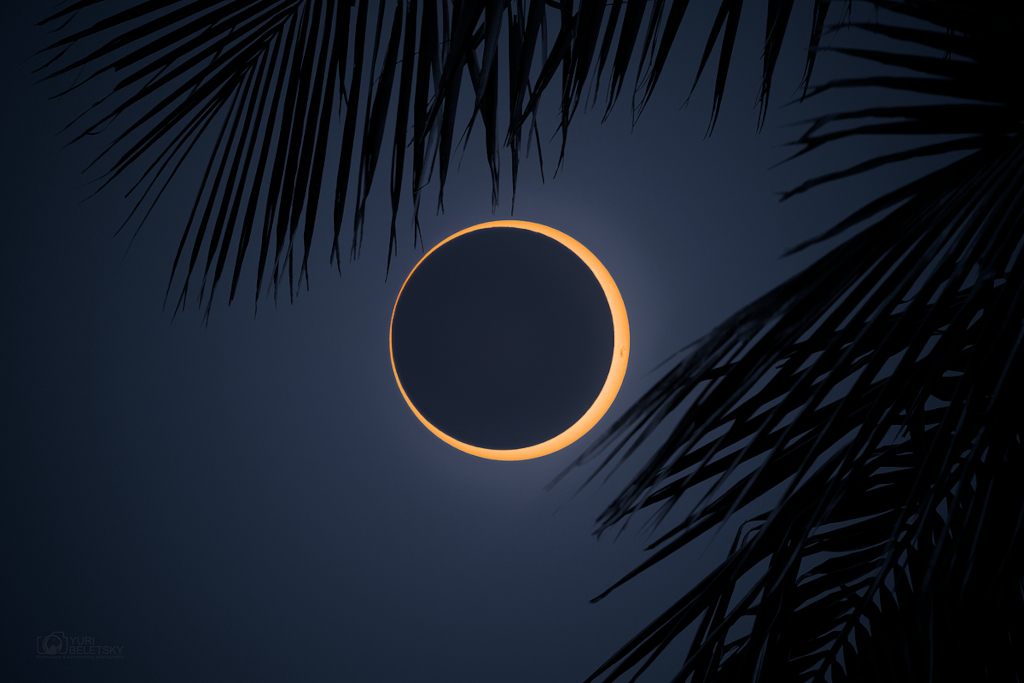
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/12/2024 3:04 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Yuri Beletsky (Carnegie Las Campanas Observatory, TWAN) Explanation: The second solar eclipse of 2024 began in the Pacific. On October 2nd the Moon's shadow swept from west to east, with an annular eclipse visible along a narrow antumbral shadow path tracking mostly over ocean, making its only major landfall near the southern tip of South America, and then ending in the southern Atlantic. The dramatic total annular eclipse phase is known to some as a ring of fire. Also tracking across islands in the southern Pacific, the Moon's antumbral shadow grazed Easter Island allowing denizens to follow all phases of the annular eclipse. Framed by palm tree leaves this clear island view is a stack of two images, one taken with and one taken without a solar filter near the moment of the maximum annular phase. The New Moon's silhouette appears just off center, though still engulfed by the bright disk of the active Sun. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5705 |
|
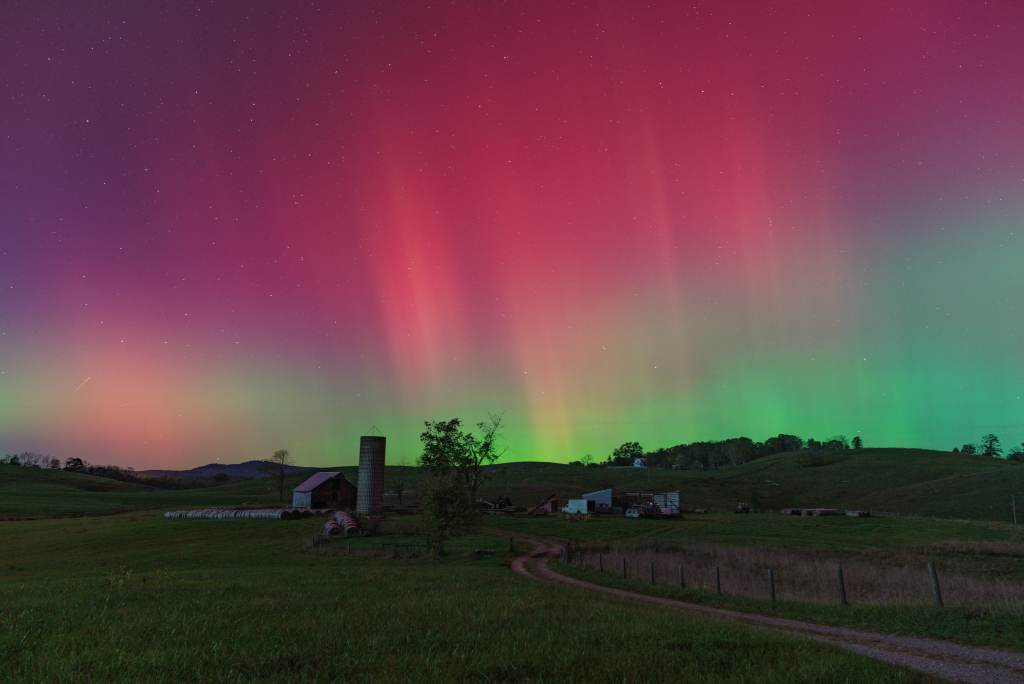
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/13/2024 1:46 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Jonathan Eggleston Explanation: A gravel country lane gently winds through this colorful rural night skyscape. Captured from Monroe County in southern West Virginia on the evening of October 10, the starry sky above is a familiar sight. Shimmering curtains of aurora borealis or northern lights definitely do not make regular appearances here, though. Surprisingly vivid auroral displays were present on that night at very low latitudes around the globe, far from their usual northern and southern high latitude realms. The extensive auroral activity was evidence of a severe geomagnetic storm triggered by the impact of a coronal mass ejection (CME), an immense magnetized cloud of energetic plasma. The CME was launched toward Earth from the active Sun following a powerful X-class solar flare. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5706 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/14/2024 2:09 AMCopy HTML 2024 October 13 Video Credit & Copyright: Cristian Bigontina Explanation: Did you see last night's aurora? This question was relevant around much of the world a few days ago because a powerful auroral storm became visible unusually far from the Earth's poles. The cause was a giant X-class solar flare on Tuesday that launched energetic electrons and protons into the Solar System, connecting to the Earth via our planet's magnetic field. A red glow of these particles striking oxygen atoms high in Earth's atmosphere pervades the frame, while vertical streaks dance. The featured video shows a one-hour timelapse as seen from Cortina d'Ampezzo over Alps Mountain peaks in northern Italy. Stars from our Milky Way Galaxy dot the background while streaks from airplanes and satellites punctuate the foreground. The high recent activity of our Sun is likely to continue to produce picturesque auroras over Earth during the next year or so. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5707 |
|
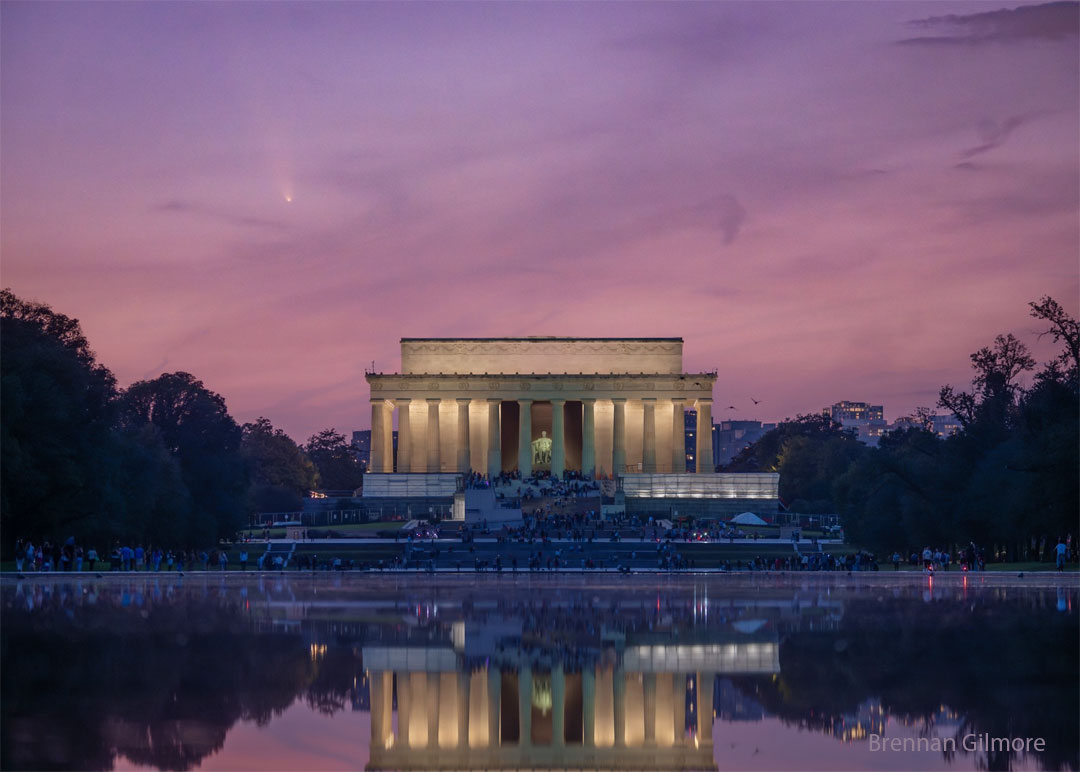
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/15/2024 2:36 AMCopy HTML Credit & Copyright: Brennan Gilmore Explanation: Go outside at sunset tonight and see a comet! C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) has become visible in the early evening sky in northern locations to the unaided eye. To see the comet, look west through a sky with a low horizon. If the sky is clear and dark enough, you will not even need binoculars -- the faint tail of the comet should be visible just above the horizon for about an hour. Pictured, Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS was captured two nights ago over the Lincoln Memorial monument in Washington, DC, USA. With each passing day at sunset, the comet and its changing tail should be higher and higher in the sky, although exactly how bright and how long its tails will be can only be guessed. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5708 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/16/2024 3:27 AMCopy HTML 2024 October 15 Credit & Copyright: Nico Lefaudeux Explanation: How bright and strange will the tails of Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS become? The comet has brightened dramatically over the few weeks as it passed its closest to the Sun and, just three days ago, passed its closest to the Earth. C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) became of the brightest comets of the past century over the past few days, but was unfortunately hard to see because it was so nearly superposed on the Sun. As the comet appears to move away from the Sun, it is becoming a remarkable sight -- but may soon begin to fade. The featured animated video shows how the comet's tails have developed, as viewed from Earth, and gives one prediction about how they might further develop. As shown in the video, heavier parts of the dust tail that trails the comet have begun to appear to point in nearly the opposite direction from lighter parts of the dust tail as well as the comet's ion tail, the blue tail that is pushed directly out from the Sun by the solar wind. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5709 |
|
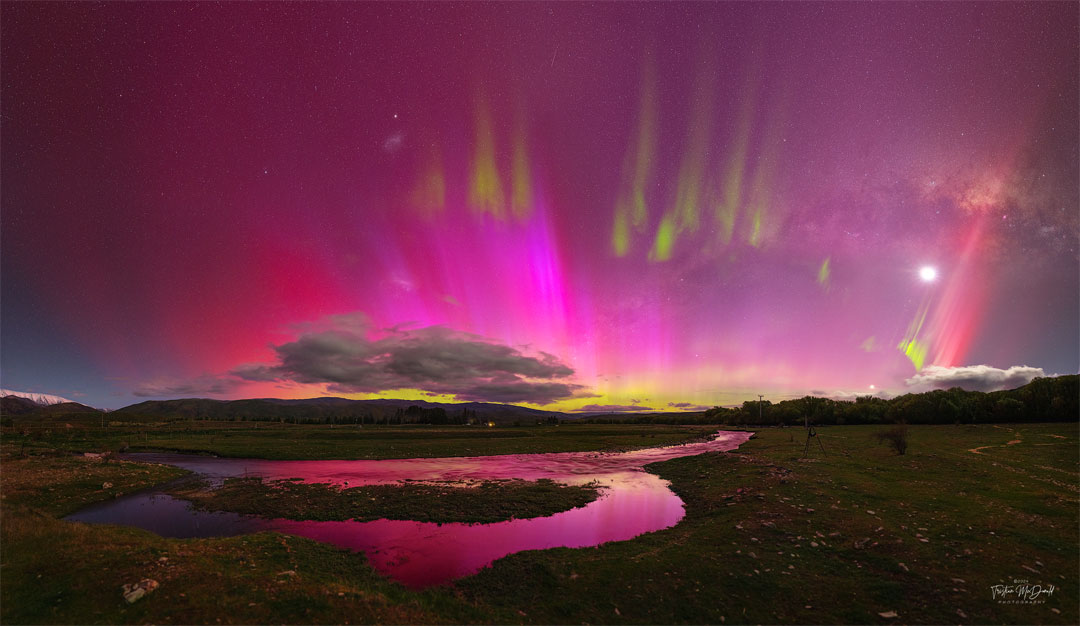
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/17/2024 3:04 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Tristian McDonald Explanation: Sometimes the night sky is full of surprises. Take the sky over Lindis Pass, South Island, New Zealand one-night last week. Instead of a typically calm night sky filled with constant stars, a busy and dynamic night sky appeared. Suddenly visible were pervasive red aurora, green picket-fence aurora, a red SAR arc, a STEVE, a meteor, and the Moon. These outshone the center of our Milky Way Galaxy and both of its two satellite galaxies: the LMC and SMC. All of these were captured together on 28 exposures in five minutes, from which this panorama was composed. Auroras lit up many skies last week, as a Coronal Mass Ejection from the Sun unleashed a burst of particles toward our Earth that created colorful skies over latitudes usually too far from the Earth's poles to see them. More generally, night skies this month have other surprises, showing not only auroras -- but comets. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5710 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/17/2024 3:04 AMCopy HTML
|
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5711 |
|
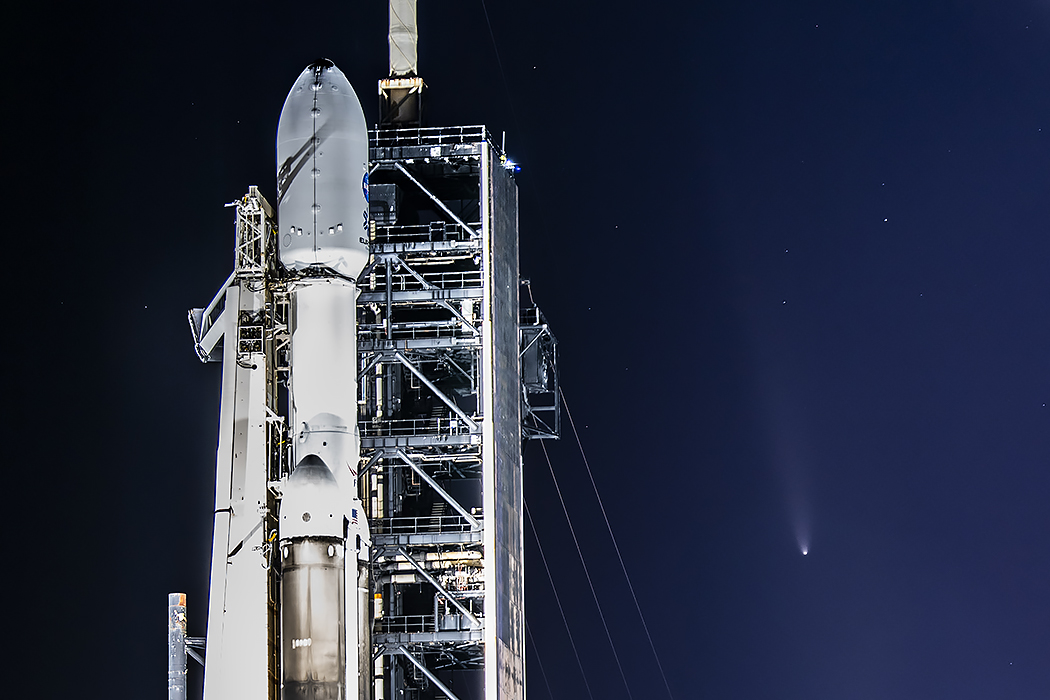
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/18/2024 1:46 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Ben Cooper (Launch Photography) Explanation: NASA's Europa Clipper is now headed toward an ocean world beyond Earth. The large spacecraft is tucked into the payload fairing atop the Falcon Heavy rocket in this photo, taken at Kennedy Space Center the day before the mission's successful October 14 launch. Europa Clipper's interplanetary voyage will first take it to Mars, then back to Earth, and then on to Jupiter on gravity assist trajectories that will allow it to enter orbit around Jupiter in April 2030. Once orbiting Jupiter, the spacecraft will fly past Europa 49 times, exploring a Jovian moon with a global subsurface ocean that may have conditions to support life. Posing in the background next to the floodlit rocket is Comet Tsuchinsan-ATLAS, about a day after the comet's closest approach to Earth. A current darling of evening skies, the naked-eye comet is a visitor from the distant Oort cloud |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5712 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/19/2024 3:32 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Adam Block Explanation: On October 14 it was hard to capture a full view of Comet C/2023 A3 Tsuchinshan-ATLAS. Taken after the comet's closest approach to our fair planet, this evening skyview almost does though. With two telephoto frames combined, the image stretches about 26 degrees across the sky from top to bottom, looking west from Gates Pass, Tucson, Arizona. Comet watchers that night could even identify globular star cluster M5 and the faint apparition of periodic comet 13P Olbers near the long the path of Tsuchinshan-ATLAS's whitish dust tail above the bright comet's coma. Due to perspective as the Earth is crossing the comet's orbital plane, Tsuchinshan-ATLAS also has a pronounced antitail. The antitail is composed of dust previously released and fanning out away from the Sun along the comet's orbit, visible as a needle-like extension below the bright coma toward the rugged western horizon. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5713 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/20/2024 2:29 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Xingyang Cai Explanation: These six panels follow daily apparitions of comet C/2023 A3 Tsuchinshan-ATLAS as it moved away from our fair planet during the past week. The images were taken with the same camera and lens at the indicated dates and locations from California, planet Earth. At far right on October 12 the visitor from the distant Oort cloud was near its closest approach, some 70 million kilometers (about 4 light-minutes) away. Its bright coma and long dust tail were close on the sky to the setting Sun but still easy to spot against a bright western horizon. Over the following days, the outbound comet steadily climbs above the ecliptic and north into the darker western evening sky, but begins to fade from view. Crossing the Earth's orbital plane around October 14, Tsuchinshan-ATLAS exhibits a noticeable antitail extended toward the western horizon. Higher in the evening sky at sunset by October 17 (far left) the comet has faded and reached a distance of around 77 million kilometers from planet Earth. Hopefully you enjoyed some of Tsuchinshan-ATLAS's bid to become the best comet of 2024. This comet's initial orbital period estimates were a mere 80,000 years, but in fact it may never return to the inner Solar System. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5714 |
|
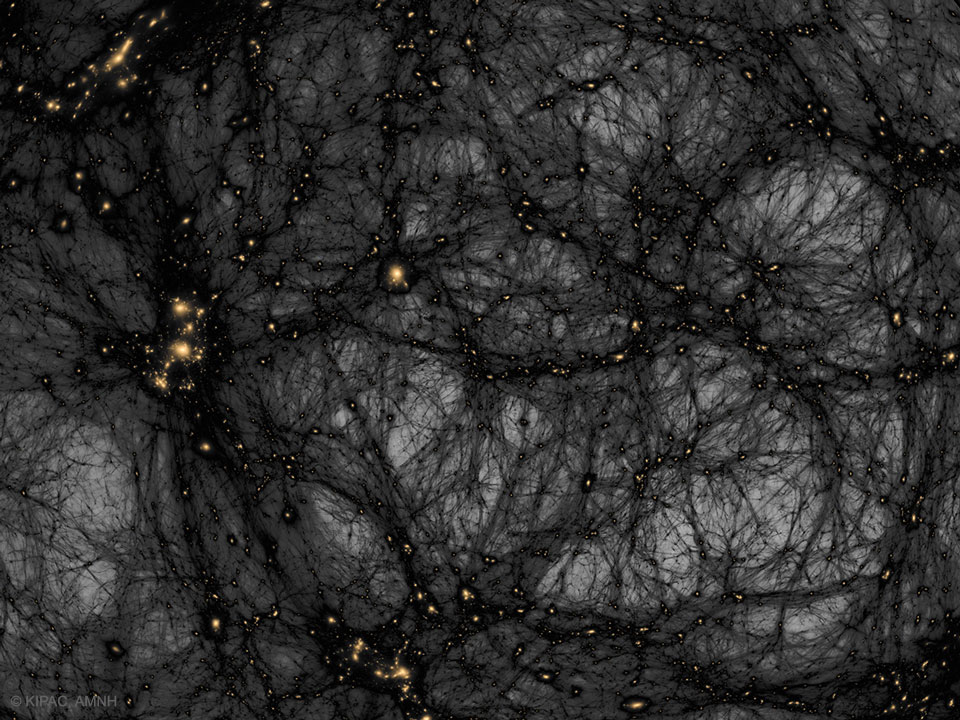
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/21/2024 2:22 AMCopy HTML Illustration Credit & Copyright: Tom Abel & Ralf Kaehler (KIPAC, SLAC), AMNH Explanation: Is our universe haunted? It might look that way on this dark matter map. The gravity of unseen dark matter is the leading explanation for why galaxies rotate so fast, why galaxies orbit clusters so fast, why gravitational lenses so strongly deflect light, and why visible matter is distributed as it is both in the local universe and on the cosmic microwave background. The featured image from the American Museum of Natural History's Hayden Planetarium Space Show Dark Universe highlights one example of how pervasive dark matter might haunt our universe. In this frame from a detailed computer simulation, complex filaments of dark matter, shown in black, are strewn about the universe like spider webs, while the relatively rare clumps of familiar baryonic matter are colored orange. These simulations are good statistical matches to astronomical observations. In what is perhaps a scarier turn of events, dark matter -- although quite strange and in an unknown form -- is no longer thought to be the strangest source of gravity in the universe. That honor now falls to dark energy, a more uniform source of repulsive gravity that seems to now dominate the expansion of the entire universe. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5715 |
|
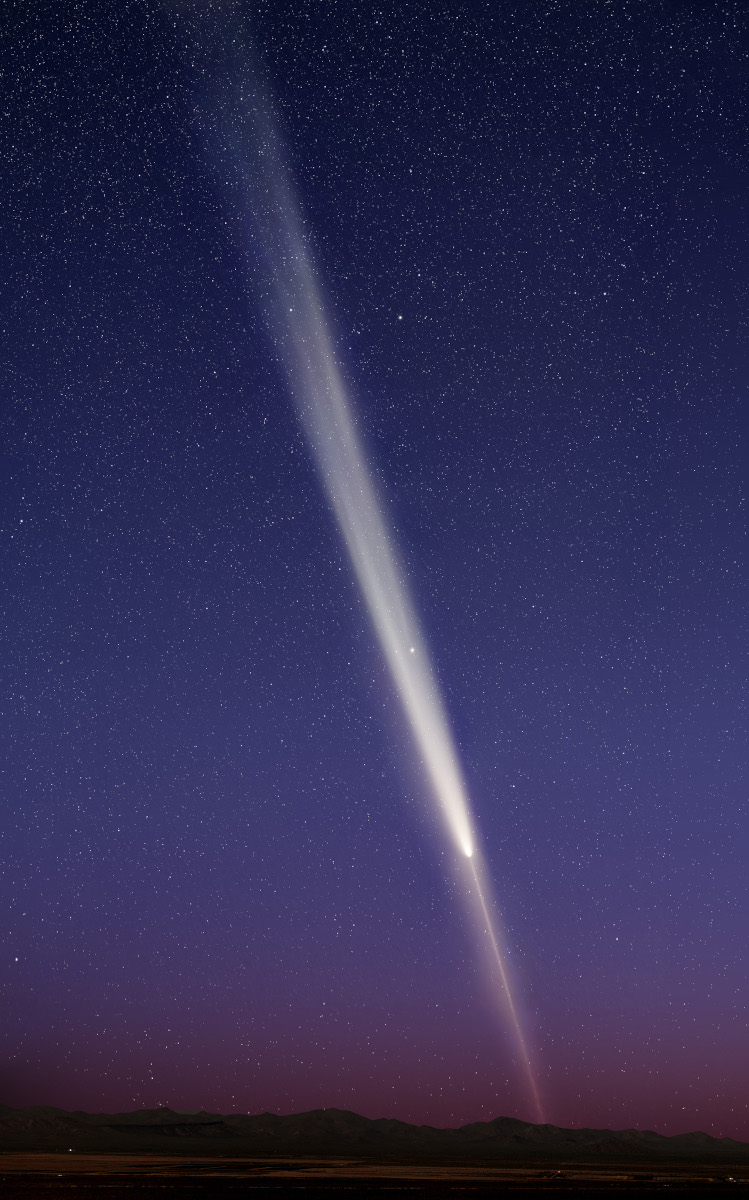
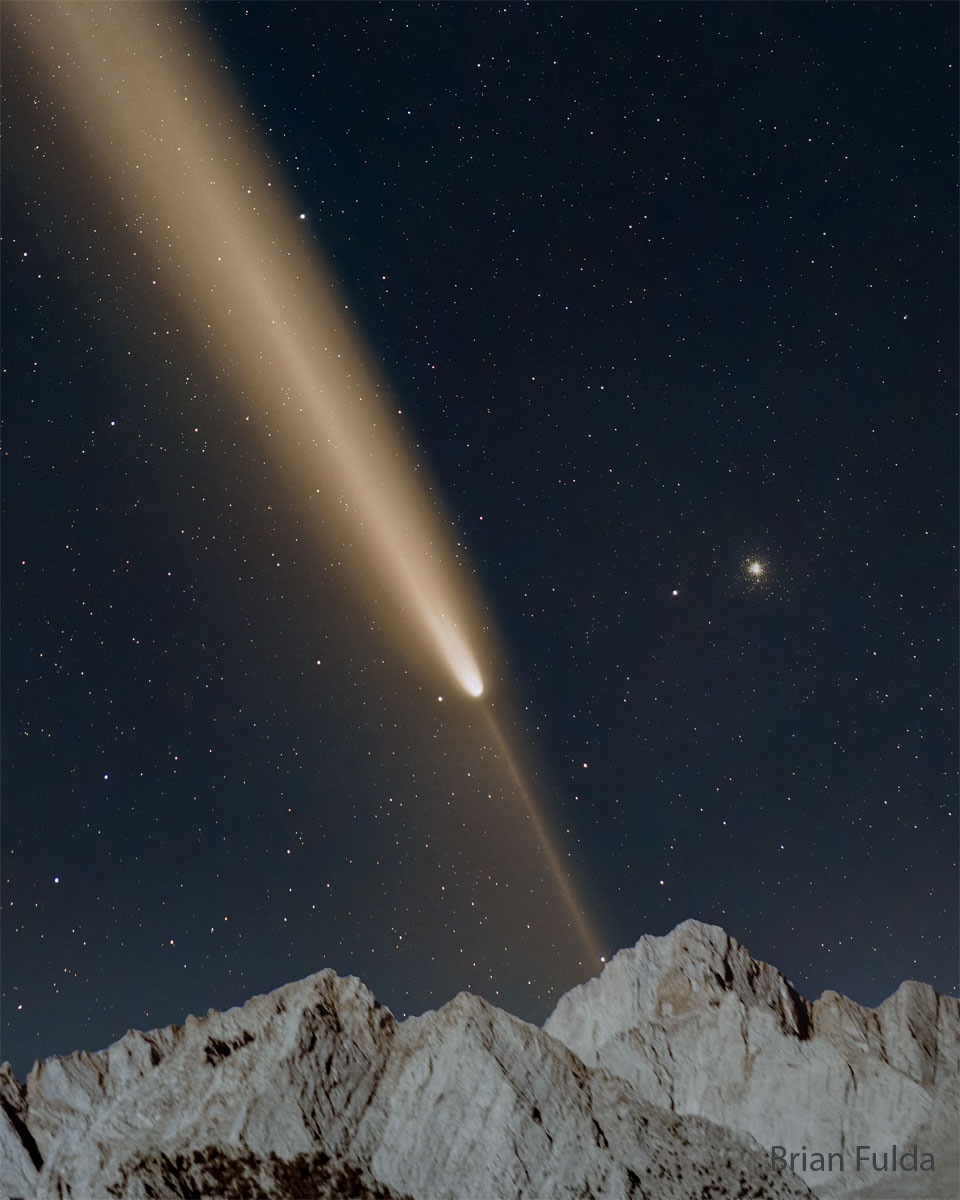
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/22/2024 2:30 AMCopy HTML Credit & Copyright: Brian Fulda Explanation: The tails of Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS were a sight to behold. Pictured, C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) was captured near peak impressiveness last week over the Eastern Sierra Mountains in California, USA. The comet not only showed a bright tail, but a distinct anti-tail pointing in nearly the opposite direction. The globular star cluster M5 can be seen on the right, far in the distance. As it approached, it was unclear if this crumbling iceberg would disintegrate completely as it warmed in the bright sunlight. In reality, the comet survived to become brighter than any star in the night (magnitude -4.9), but unfortunately was then so nearly in front of the Sun that it was hard for many casual observers to locate. Whether Comet Tsuchinshan-Atlas becomes known as the Great Comet of 2024 now depends, in part, on how impressive incoming comet C/2024 S1 (ATLAS) becomes over the next two weeks. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5716 |
|
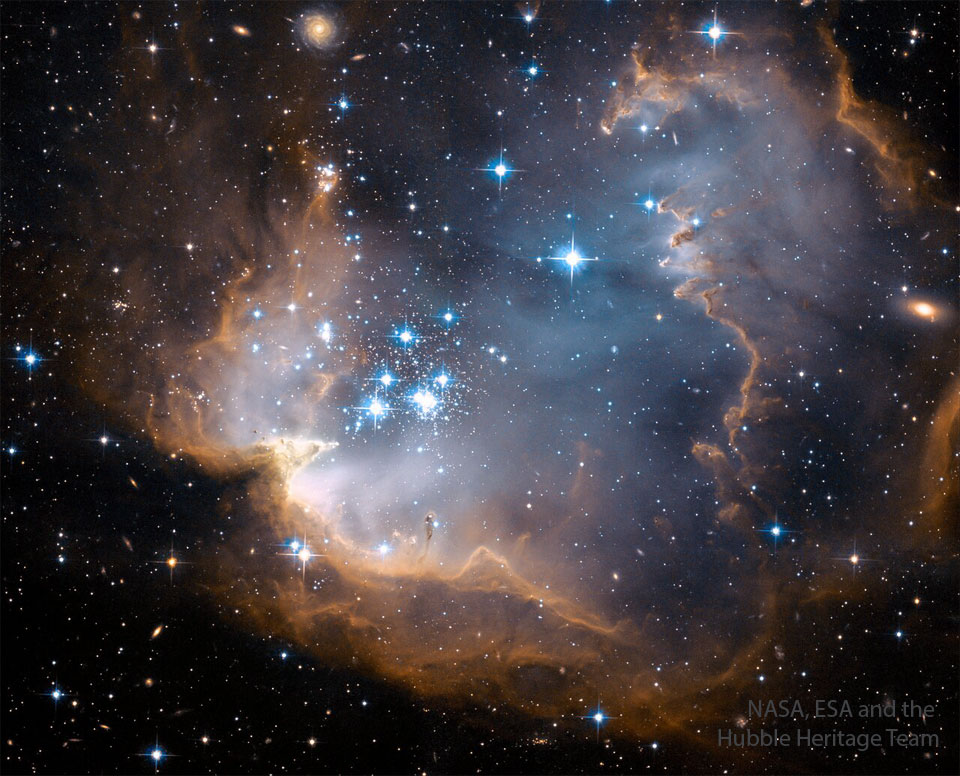
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/23/2024 1:36 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI; Processing: Diego Pisano Explanation: These dark pillars may look destructive, but they are creating stars. This pillar-capturing picture of the Eagle Nebula combines visible light exposures taken with the Hubble Space Telescope with infrared images taken with the James Webb Space Telescope to highlight evaporating gaseous globules (EGGs) emerging from pillars of molecular hydrogen gas and dust. The giant pillars are light years in length and are so dense that interior gas contracts gravitationally to form stars. At each pillar's end, the intense radiation of bright young stars causes low density material to boil away, leaving stellar nurseries of dense EGGs exposed. The Eagle Nebula, associated with the open star cluster M16, lies about 7000 light years away. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5717 |
|
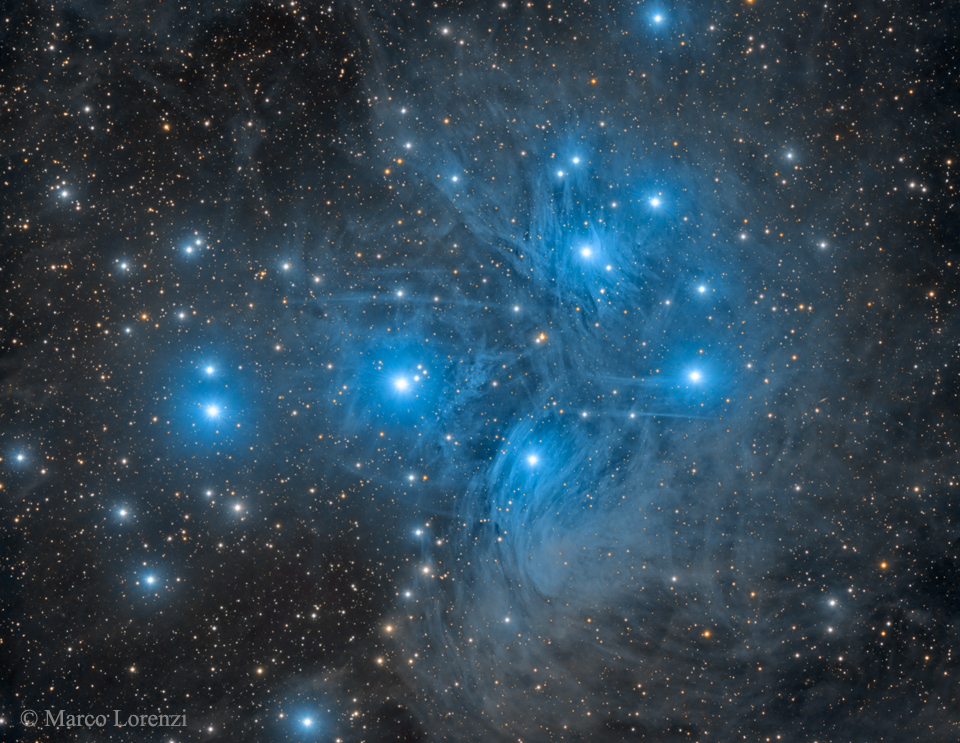
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/24/2024 3:00 AMCopy HTML 2024 October 23 Image Credit & Copyright: Marco Lorenzi (Glittering Lights) Explanation: Have you ever seen the Pleiades star cluster? Even if you have, you probably have never seen it as dusty as this. Perhaps the most famous star cluster on the sky, the bright stars of the Pleiades can be seen without binoculars from even the depths of a light-polluted city. With a long exposure from a dark location, though, the dust cloud surrounding the Pleiades star cluster becomes very evident. The featured exposure took over 12 hours and covers a sky area several times the size of the full moon. Also known as the Seven Sisters and M45, the Pleiades lies about 400 light years away toward the constellation of the Bull (Taurus). A common legend with a modern twist is that one of the brighter stars faded since the cluster was named, leaving only six stars visible to the unaided eye. The actual number of Pleiades stars visible, however, may be more or less than seven, depending on the darkness of the surrounding sky and the clarity of the observer's eyesight. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5718 |
|
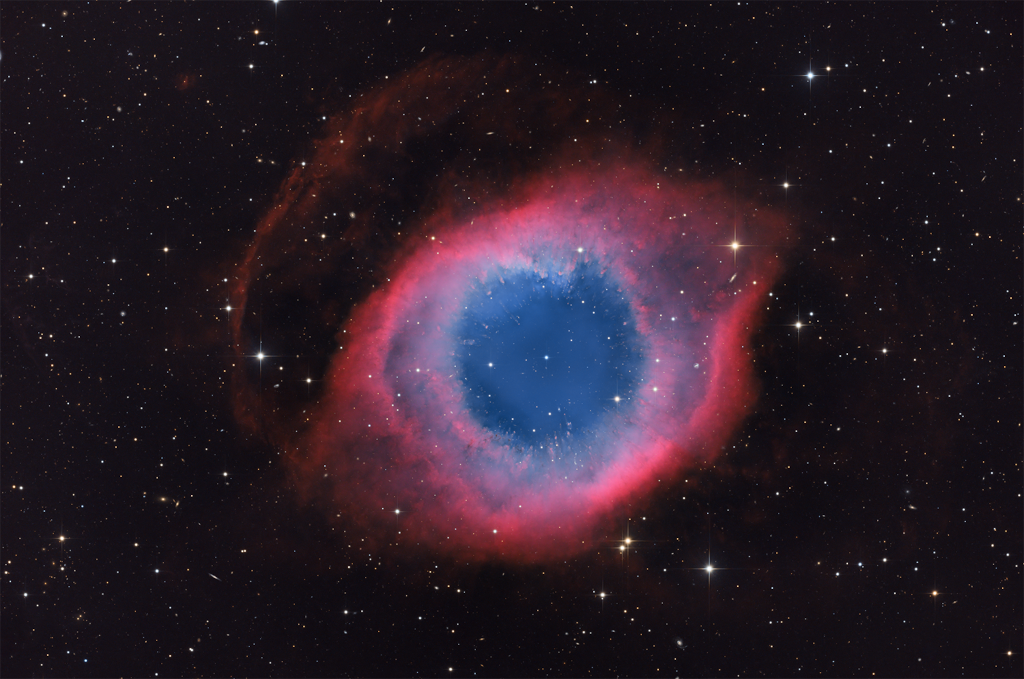
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/25/2024 2:27 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Patrick Winkler Explanation: A mere seven hundred light years from Earth toward the constellation Aquarius, a star is dying. The once sun-like star's last few thousand years have produced the Helix Nebula. Also known as NGC 7293, the cosmic Helix is a well studied and nearby example of a Planetary Nebula, typical of this final phase of stellar evolution. Combining narrow band data from emission lines of hydrogen atoms in red and oxygen atoms in blue-green hues, this deep image shows tantalizing details of the Helix, including its bright inner region about 3 light-years across. The white dot at the Helix's center is this Planetary Nebula's hot, dying central star. A simple looking nebula at first glance, the Helix is now understood to have a surprisingly complex geometry. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5719 |
|
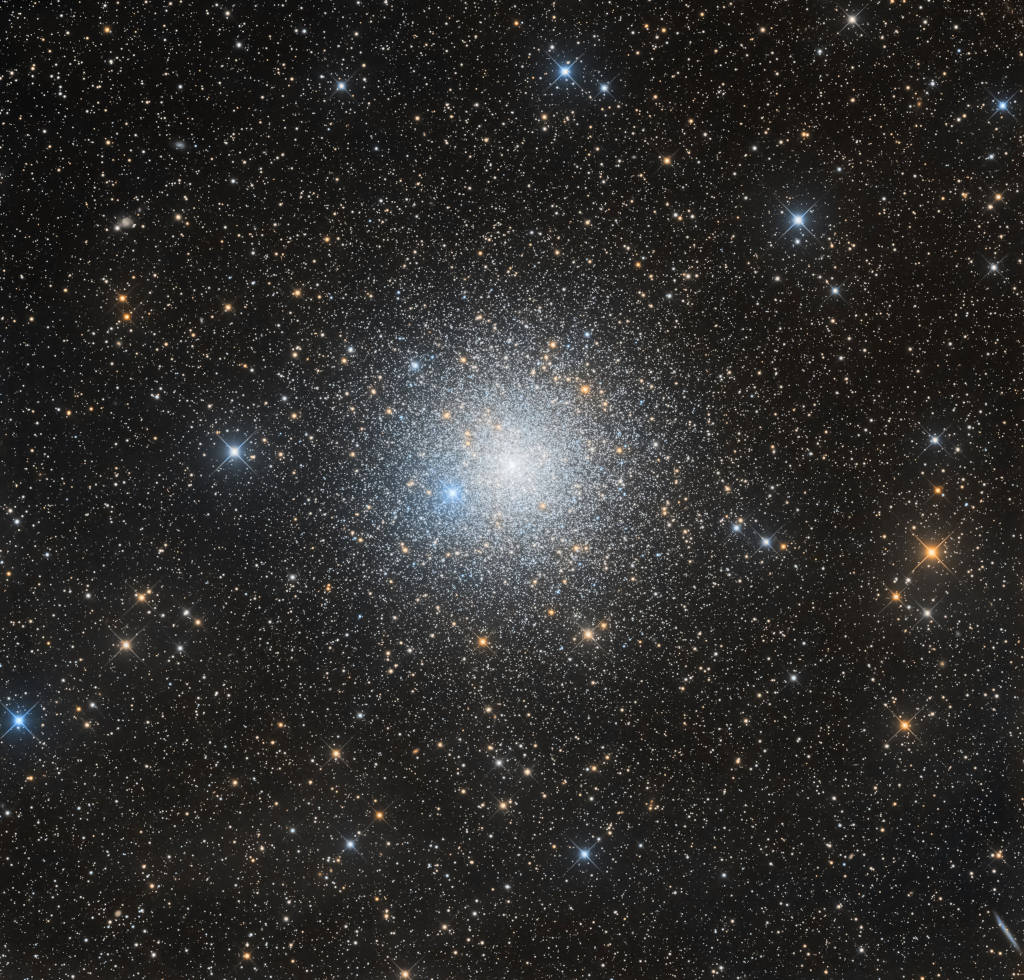
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/26/2024 3:05 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Massimo Di Fusco, Aygen Erkaslan Explanation: Some 13,000 light-years away toward the southern constellation Pavo, the globular star cluster NGC 6752 roams the halo of our Milky Way galaxy. Over 10 billion years old, NGC 6752 follows clusters Omega Centauri, 47 Tucanae, and Messier 22 as the fourth brightest globular in planet Earth's night sky. It holds over 100 thousand stars in a sphere about 100 light-years in diameter. Telescopic explorations of NGC 6752 have found that a remarkable fraction of the stars near the cluster's core, are multiple star systems. They also reveal the presence of blue straggle stars, stars which appear to be too young and massive to exist in a cluster whose stars are all expected to be at least twice as old as the Sun. The blue stragglers are thought to be formed by star mergers and collisions in the dense stellar environment at the cluster's core. This sharp color composite also features the cluster's ancient red giant stars in yellowish hues. (Note: The bright, spiky blue star about 8 o'clock from the cluster center is a foreground star along the line-of-sight to NGC 6752) |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5720 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/27/2024 2:32 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Christophe Vergnes, Hervé Laur Explanation: These brightly outlined flowing shapes look ghostly on a cosmic scale. A telescopic view toward the constellation Cassiopeia, the colorful skyscape features the swept-back, comet-shaped clouds IC 59 (left) and IC 63. About 600 light-years distant, the clouds aren't actually ghosts. They are slowly disappearing though, under the influence of energetic radiation from hot, luminous star gamma Cas. Gamma Cas is physically located only 3 to 4 light-years from the nebulae and lies just above the right edge of the frame. Slightly closer to gamma Cas, IC 63 is dominated by red H-alpha light emitted as hydrogen atoms ionized by the hot star's ultraviolet radiation recombine with electrons. Farther from the star, IC 59 shows less H-alpha emission but more of the characteristic blue tint of dust reflected star light. The field of view spans over 1 degree or 10 light-years at the estimated distance of the interstellar apparitions. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5721 |
|
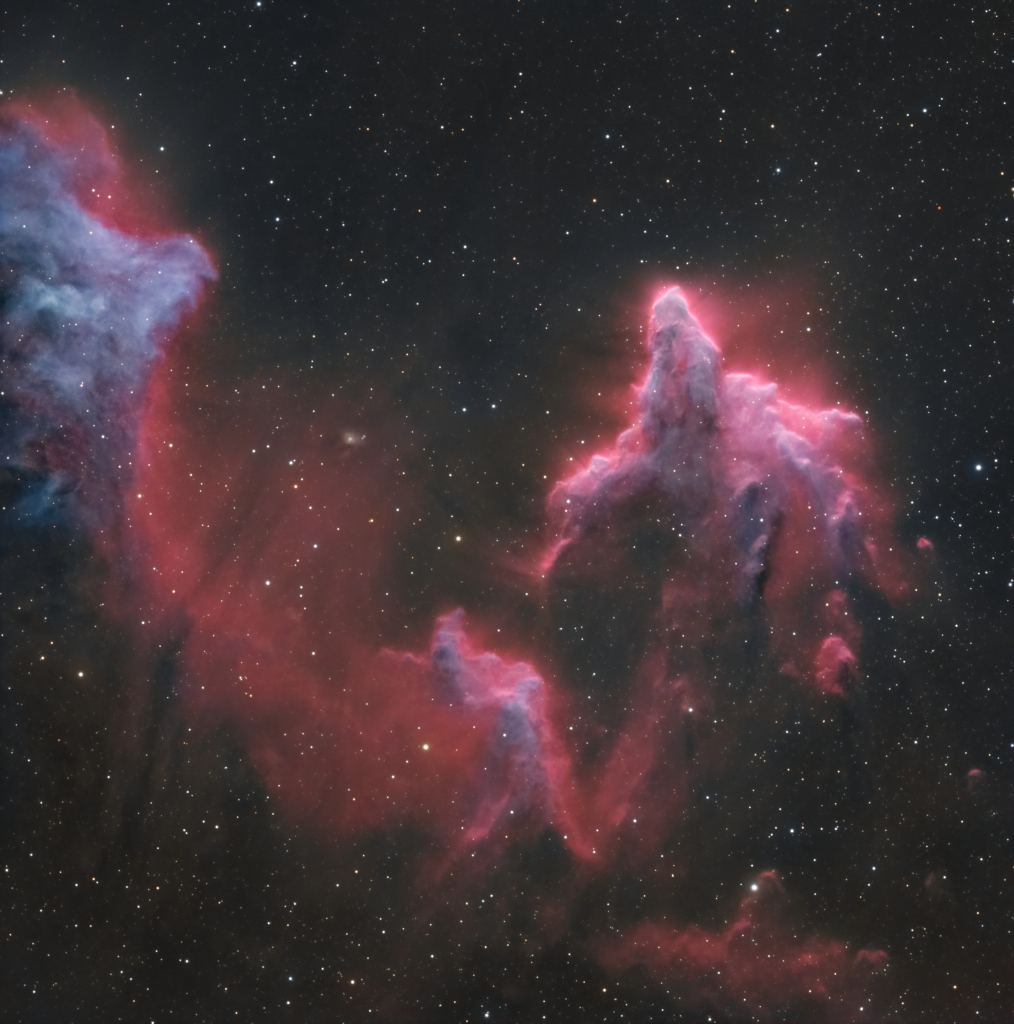
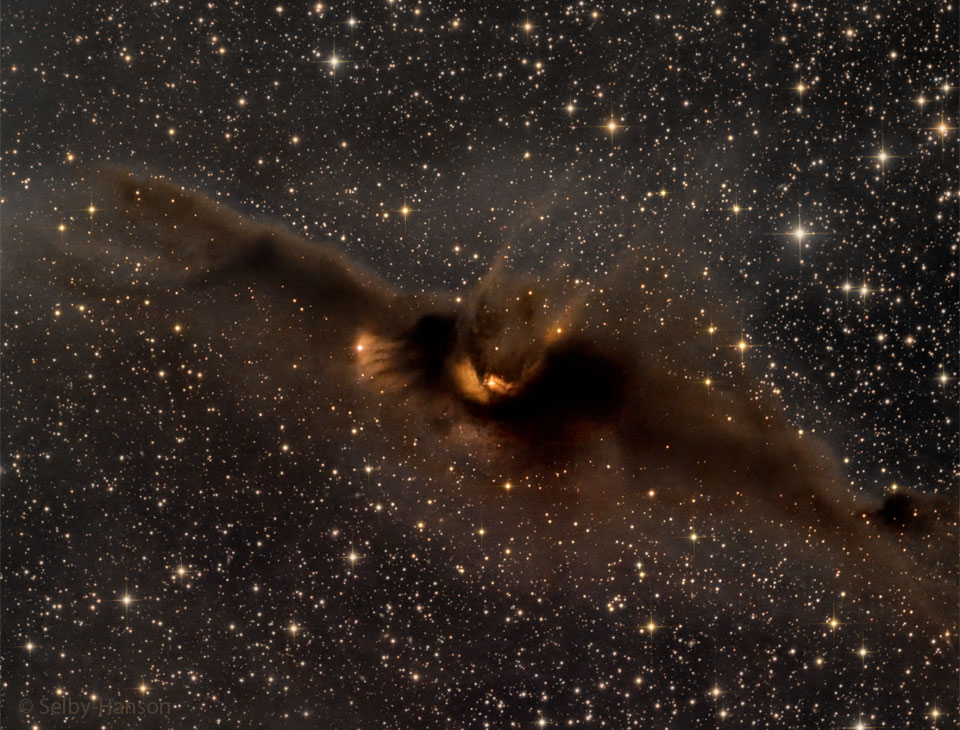
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/28/2024 2:55 AMCopy HTML Credit & Copyright: Mark Hanson and Mike Selby; Text: Michelle Thaller (NASA's GSFC) Explanation: What is the most spook-tacular nebula in the galaxy? One contender is LDN 43, which bears an astonishing resemblance to a vast cosmic bat flying amongst the stars on a dark Halloween night. Located about 1400 light years away in the constellation Ophiuchus, this molecular cloud is dense enough to block light not only from background stars, but from wisps of gas lit up by the nearby reflection nebula LBN 7. Far from being a harbinger of death, this 12-light year-long filament of gas and dust is actually a stellar nursery. Glowing with eerie light, the bat is lit up from inside by dense gaseous knots that have just formed young stars. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5722 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/29/2024 2:51 AMCopy HTML Credit & Copyright: Louis LEROUX-GÉRÉ Explanation: Sometimes a river of hot gas flows over your head. In this case the river created a Strong Thermal Emission Velocity Enhancement (STEVE) that glowed bright red, white, and pink. Details of how STEVEs work remain a topic of research, but recent evidence holds that their glow results from a fast-moving river of hot ions flowing over a hundred kilometers up in the Earth's atmosphere: the ionosphere. The more expansive dull red glow might be related to the flowing STEVE, but alternatively might be a Stable Auroral Red (SAR) arc, a more general heat-related glow. The featured picture, taken earlier this month in Côte d'Opale, France, is a wide-angle digital composite made as the STEVE arc formed nearly overhead. Although the apparition lasted only a few minutes, this was long enough for the quick-thinking astrophotographer to get in the picture -- can you find him? |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5723 |
|
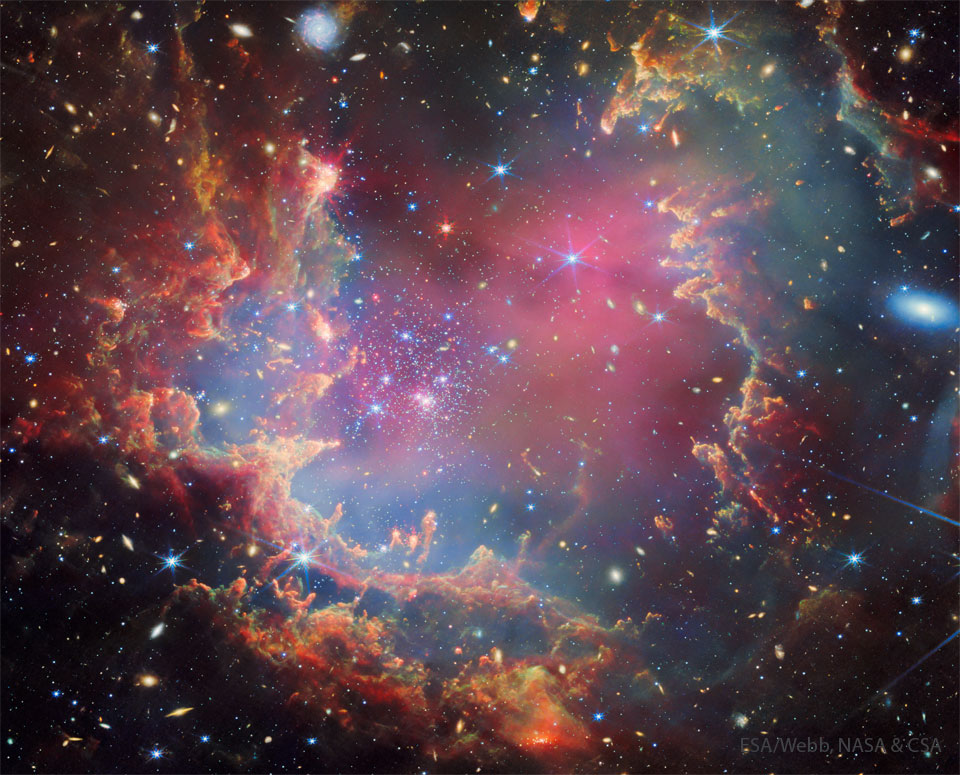
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/30/2024 1:50 AMCopy HTML Credit: ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, P. Zeidler, E. Sabbi, A. Nota, M. Zamani (ESA/Webb) Explanation: The stars are destroying the pillars. More specifically, some of the newly formed stars in the image center are emitting light so energetic that is evaporating the gas and dust in the surrounding pillars. Simultaneously, the pillars themselves are still trying to form new stars. The whole setting is the star cluster NGC 602, and this new vista was taken by the Webb Space Telescope in multiple infrared colors. In comparison, a roll-over image shows the same star cluster in visible light, taken previously by the Hubble Space Telescope. NGC 602 is located near the perimeter of the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), a small satellite galaxy of our Milky Way galaxy. At the estimated distance of the SMC, the featured picture spans about 200 light-years. A tantalizing assortment of background galaxies are also visible -- mostly around the edges -- that are at least hundreds of millions of light-years beyond. |
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5724 |
|
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/30/2024 1:51 AMCopy HTML
|
|
|
Niceguy2
|
#5725 |
|
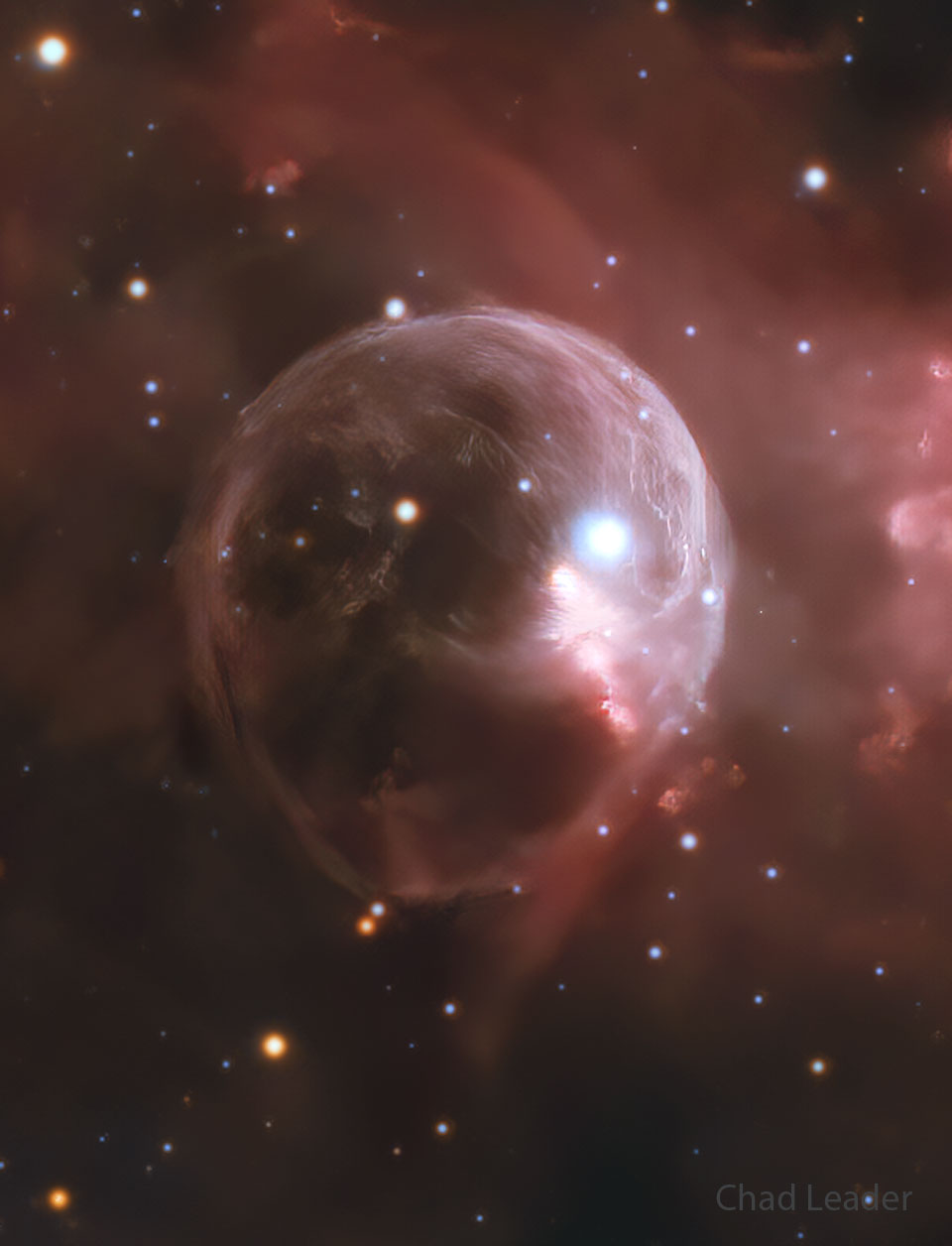
Re:Astronomy Picture of the Day Date Posted:10/31/2024 2:46 AMCopy HTML Credit & Copyright: Chad Leader Explanation: What created this huge space bubble? Blown by the wind from a star, this tantalizing, head-like apparition is cataloged as NGC 7635, but known simply as the Bubble Nebula. The featured striking view utilizes a long exposure to reveal the intricate details of this cosmic bubble and its environment. Although it looks delicate, the 10 light-year diameter bubble offers evidence of violent processes at work. Seen here above and right of the Bubble's center, a bright hot star is embedded in the nebula's reflecting dust. A fierce stellar wind and intense radiation from the star, which likely has a mass 10 to 20 times that of the Sun, has blasted out the structure of glowing gas against denser material in a surrounding molecular cloud. The intriguing Bubble Nebula lies a mere 11,000 light-years away toward the boastful constellation Cassiopeia. |